Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the ttk styles, how to use and customize the widget’s styles, and how to change the appearance of a widget by extending the built-in styles.
Introduction to the ttk styles #
A theme of a collection of styles that determine the appearances of ttk widgets.
A style is a description of the appearance of a widget class. Typically, a theme comes with a predefined set of styles.
Therefore, to change the appearance of ttk widgets, you can:
- Modify the built-in styles
- Create new styles
Generally, the style name of a ttk widget starts with the letter 'T' followed by the widget name, for example, TLabel and TButton.
In Tkinter, every widget has a default widget class. A widget class defines the default style for a widget.
The following table shows the style names of the common ttk widget classes:
| Widget class | Style name |
|---|---|
Button | TButton |
Checkbutton | TCheckbutton |
Combobox | TCombobox |
Entry | TEntry |
Frame | TFrame |
Label | TLabel |
LabelFrame | TLabelFrame |
Menubutton | TMenubutton |
Notebook | TNotebook |
PanedWindow | TPanedwindow |
Progressbar* | Horizontal.TProgressbar or Vertical.TProgressbar, depending on the orient option. |
Radiobutton | TRadiobutton |
Scale* | Horizontal.TScale or Vertical.TScale, depending on the orient option. |
Scrollbar* | Horizontal.TScrollbar or Vertical.TScrollbar, depending on the orient option |
Separator | TSeparator |
Sizegrip | TSizegrip |
Treeview* | Treeview |
(*) The style names of the Progressbar , Scale, Scrollbar, and Treeview widgets don’t start with the letter T.
At runtime, you can get the widget class of a widget by calling the winfo_class() method of the widget instance.
The following example uses the winfo_class() method to get the widget class of a button widget:
button = ttk.Button(root, text='Click Me')
print(button.winfo_class())Code language: Python (python)Output:
TButtonCode language: Python (python)Modifying built-in ttk styles #
Every style has a set of options that define the widget’s appearance.
To modify the appearance of a style, you use the configure() method of the Style class:
style = ttk.Style(root)
style.configure(style_name, **options)Code language: Python (python)The following program shows how to change the font of all the Label and Button widgets by modifying the TLabel and TButton‘s styles:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry('300x110')
self.resizable(0, 0)
self.title('Login')
# UI options
paddings = {'padx': 5, 'pady': 5}
entry_font = {'font': ('Helvetica', 11)}
# configure the grid
self.columnconfigure(0, weight=1)
self.columnconfigure(1, weight=3)
username = tk.StringVar()
password = tk.StringVar()
# username
username_label = ttk.Label(self, text="Username:")
username_label.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.W, **paddings)
username_entry = ttk.Entry(self, textvariable=username, **entry_font)
username_entry.grid(column=1, row=0, sticky=tk.E, **paddings)
# password
password_label = ttk.Label(self, text="Password:")
password_label.grid(column=0, row=1, sticky=tk.W, **paddings)
password_entry = ttk.Entry(
self, textvariable=password, show="*", **entry_font)
password_entry.grid(column=1, row=1, sticky=tk.E, **paddings)
# login button
login_button = ttk.Button(self, text="Login")
login_button.grid(column=1, row=3, sticky=tk.E, **paddings)
# configure style
self.style = ttk.Style(self)
self.style.configure('TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 11))
self.style.configure('TButton', font=('Helvetica', 11))
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
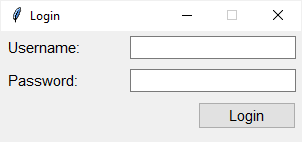
How it works.
First, create a new instance of the ttk.Style class:
self.style = ttk.Style(self)
Code language: Python (python)Second, change the font of the TLabel and TButton‘s styles using the configure() method of the Style object:
self.style.configure('TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 12))
self.style.configure('TButton', font=('Helvetica', 12))Code language: Python (python)Extending built-in ttk styles #
To create a new style that is derived from a built-in style, you use the style name like this:
new_style.builtin_styleCode language: Python (python)For example, to create a new style of the Label widget used for displaying a heading, you can name it as follows:
Heading.TLabelCode language: Python (python)The Heading.TLabel style inherits all options from the built-in TLabel style.
To override a specific option, you also use the configure() method of the Style class:
style = ttk.Style(self)
style.configure(custom_style, **options)Code language: Python (python)The following example adds a heading to the login window. The heading has the style derived from the TLabel style:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry('300x150')
self.resizable(0, 0)
self.title('Login')
# UI options
paddings = {'padx': 5, 'pady': 5}
entry_font = {'font': ('Helvetica', 11)}
# configure the grid
self.columnconfigure(0, weight=1)
self.columnconfigure(1, weight=3)
username = tk.StringVar()
password = tk.StringVar()
# heading
heading = ttk.Label(self, text='Member Login', style='Heading.TLabel')
heading.grid(column=0, row=0, columnspan=2, pady=5, sticky=tk.N)
# username
username_label = ttk.Label(self, text="Username:")
username_label.grid(column=0, row=1, sticky=tk.W, **paddings)
username_entry = ttk.Entry(self, textvariable=username, **entry_font)
username_entry.grid(column=1, row=1, sticky=tk.E, **paddings)
# password
password_label = ttk.Label(self, text="Password:")
password_label.grid(column=0, row=2, sticky=tk.W, **paddings)
password_entry = ttk.Entry(
self, textvariable=password, show="*", **entry_font)
password_entry.grid(column=1, row=2, sticky=tk.E, **paddings)
# login button
login_button = ttk.Button(self, text="Login")
login_button.grid(column=1, row=3, sticky=tk.E, **paddings)
# configure style
self.style = ttk.Style(self)
self.style.configure('TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 11))
self.style.configure('TButton', font=('Helvetica', 11))
# heading style
self.style.configure('Heading.TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 12))
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
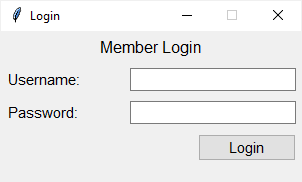
How it works.
First, add a heading to the window and assign the style Heading.TLabel to the style option of the Label widget:
heading = ttk.Label(self, text='Member Login', style='Heading.TLabel')Code language: Python (python)Then, change the font of the Heading.TLabel style to Helvetica, 12 pixels:
self.style.configure('Heading.TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 12))Code language: Python (python)Hierarchies of styles #
It’s possible to create your own entire hierarchies of styles. For example, you can have a Message.TLabel style that inherits from the built-in TLabel style.
And then you can create styles that inherit from the Message.TLabel style like Error.Message.TLabel, Warning.Message.TLabel, and Information.Message.TLabel.
When you use a particular style e.g., Error.Message.TLabel, ttk looks for options in the Error.Message.TLabel style first. If it doesn’t find the options, it’ll search in the Message.TLabel style. And it continues searching for the options in the TLabel style.
The following picture illustrates the example of the style hierarchy:
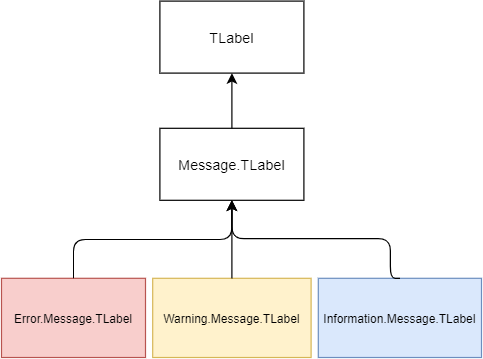
The root style determines the appearance of all widgets. The name of the root style is '.'.
For example, if you want to change the text to a 12-pixel Helvetica font for all widgets, you can configure it as follows:
style = ttk.Style(root)
style.configure('.', font=('Helvetica', 12))Code language: Python (python)Summary #
- A theme of a collection of styles. A style is a description of the appearance of a widget.
- Use the
widget.winfo_class()method to get the widget class of a widget. The widget class defines the default style for the widget. - Use the
style.configure()method to modify the style of the widget. - To customize the built-in style, you can extend it using the style name
new_style.builtin_style.