Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the Frame tkraise() method to switch between frames in a Tkinter application.
Introduction to the Frame tkraise() method #
Typically, a Tkinter application consists of multiple frames. And you often need to switch between frames to display the one that is relevant to the user’s choice.
Tkinter allows you to stack frames on top of each other. To show a particular frame, you can simply raise one above the other in the stacking order. The top frame will be visible.
To bring a frame to the top, you use the tkraise() method of the Frame widget like this:
frame.tkraise()Code language: Python (python)The Frame tkraise() method example #
In this example, you’ll extend the temperature converter application by adding the conversion of a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
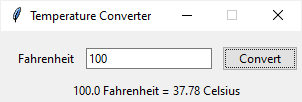
By default, the application converts a temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius.
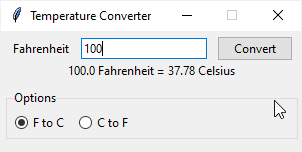
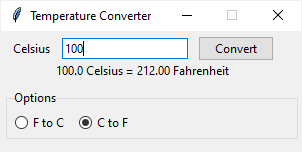
If you select the C to F radio button, the application shows a new frame that allows you to convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
To build this application, you’ll need to have three main widgets:
- A root window.
- The
ConverterFramethat shows the form fields. - And the
ControlFramethat shows the radio buttons.
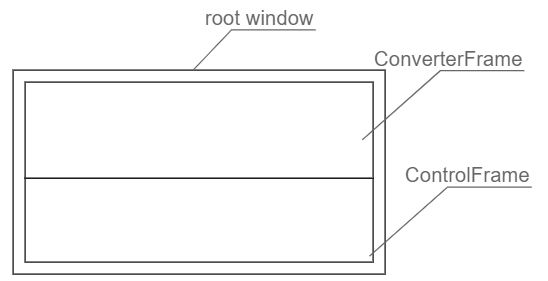
The ConverterFrame will have two instances, one that converts a temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius and the other that converts a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
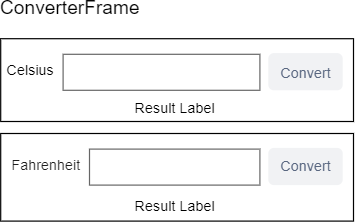
First, define a TemperatureConverter class that has two static methods: fahrenheit_to_celsius and celsius_to_fahrenheit.
class TemperatureConverter:
@staticmethod
def fahrenheit_to_celsius(f, format=True):
result = (f - 32) * 5/9
if format:
return f'{f} Fahrenheit = {result:.2f} Celsius'
return result
@staticmethod
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(c, format=True):
result = c * 9/5 + 32
if format:
return f'{c} Celsius = {result:.2f} Fahrenheit'
return result
Code language: Python (python)The fahrenheit_to_celsius and celsius_to_fahrenheit methods return a formatted string if you ignore the second argument or pass True to them. Otherwise, they’ll return the result as a number.
Second, define the ConverterFrame that will show the UI for converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius and vice versa.
To do it, you’ll need to make the ConverterFrame more flexible by adding the following parameters to the __init__() method:
- A string that will be displayed as Fahrenheit and Celsius
- A callback function for converting the temperature.
The following shows a complete ConverterFrame class:
class ConverterFrame(ttk.Frame):
def __init__(self, container, unit_from, converter):
super().__init__(container)
self.unit_from = unit_from
self.converter = converter
# field options
options = {'padx': 5, 'pady': 0}
# temperature label
self.temperature_label = ttk.Label(self, text=self.unit_from)
self.temperature_label.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky='w', **options)
# temperature entry
self.temperature = tk.StringVar()
self.temperature_entry = ttk.Entry(self, textvariable=self.temperature)
self.temperature_entry.grid(column=1, row=0, sticky='w', **options)
self.temperature_entry.focus()
# button
self.convert_button = ttk.Button(self, text='Convert')
self.convert_button.grid(column=2, row=0, sticky='w', **options)
self.convert_button.configure(command=self.convert)
# result label
self.result_label = ttk.Label(self)
self.result_label.grid(row=1, columnspan=3, **options)
# add padding to the frame and show it
self.grid(column=0, row=0, padx=5, pady=5, sticky="nsew")
def convert(self, event=None):
""" Handle button click event
"""
try:
input_value = float(self.temperature.get())
result = self.converter(input_value)
self.result_label.config(text=result)
except ValueError as error:
showerror(title='Error', message=error)
def reset(self):
self.temperature_entry.delete(0, "end")
self.result_label.text = ''Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- Use the
unit_fromargument to show the label for the temperature. - Call the
self.convertcallback in theconvert()method to convert a temperature from one unit to another. - Define the
reset()method to clear the entry widget and the result label when the frame is switched from one to another.
Third, define a ControlFrame class that shows the radio buttons for selecting a frame to show. The ControFrame class inherits from the ttk.LabelFrame.
class ControlFrame(ttk.LabelFrame):
def __init__(self, container):
super().__init__(container)
self['text'] = 'Options'
# radio buttons
self.selected_value = tk.IntVar()
ttk.Radiobutton(
self,
text='F to C',
value=0,
variable=self.selected_value,
command=self.change_frame).grid(column=0, row=0, padx=5, pady=5)
ttk.Radiobutton(
self,
text='C to F',
value=1,
variable=self.selected_value,
command=self.change_frame).grid(column=1, row=0, padx=5, pady=5)
self.grid(column=0, row=1, padx=5, pady=5, sticky='ew')
# initialize frames
self.frames = {}
self.frames[0] = ConverterFrame(
container,
'Fahrenheit',
TemperatureConverter.fahrenheit_to_celsius)
self.frames[1] = ConverterFrame(
container,
'Celsius',
TemperatureConverter.celsius_to_fahrenheit)
self.change_frame()
def change_frame(self):
frame = self.frames[self.selected_value.get()]
frame.reset()
frame.tkraise()Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- Each radio button holds a value 0 or 1.
- Create two instances of the
ConverterFrameclass, one is in charge of converting a temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius, and the other converts a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit. Also, define a dictionary to store these frames. The keys of frames are the same as the values of the radio buttons. - When a radio button is clicked, the
change_frame()method is called to select the corresponding frame from the dictionary based on the value of the selected button. - Call the
reset()method of the frame to reset the entry field and result label. And also invoke thetkraise()method to display the frame.
Fourth, define the App class that subclasses from the tk.Tk class:
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title('Temperature Converter')
self.geometry('300x120')
self.resizable(False, False)
Code language: Python (python)Finally, bootstrap the application from the if __name__ == "__main__" block:
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
ControlFrame(app)
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Put it all together.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showerror
class TemperatureConverter:
@staticmethod
def fahrenheit_to_celsius(f, format=True):
result = (f - 32) * 5/9
if format:
return f'{f} Fahrenheit = {result:.2f} Celsius'
return result
@staticmethod
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(c, format=True):
result = c * 9/5 + 32
if format:
return f'{c} Celsius = {result:.2f} Fahrenheit'
return result
class ConverterFrame(ttk.Frame):
def __init__(self, container, unit_from, converter):
super().__init__(container)
self.unit_from = unit_from
self.converter = converter
# field options
options = {'padx': 5, 'pady': 0}
# temperature label
self.temperature_label = ttk.Label(self, text=self.unit_from)
self.temperature_label.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky='w', **options)
# temperature entry
self.temperature = tk.StringVar()
self.temperature_entry = ttk.Entry(self, textvariable=self.temperature)
self.temperature_entry.grid(column=1, row=0, sticky='w', **options)
self.temperature_entry.focus()
# button
self.convert_button = ttk.Button(self, text='Convert')
self.convert_button.grid(column=2, row=0, sticky='w', **options)
self.convert_button.configure(command=self.convert)
# result label
self.result_label = ttk.Label(self)
self.result_label.grid(row=1, columnspan=3, **options)
# add padding to the frame and show it
self.grid(column=0, row=0, padx=5, pady=5, sticky="nsew")
def convert(self, event=None):
""" Handle button click event
"""
try:
input_value = float(self.temperature.get())
result = self.converter(input_value)
self.result_label.config(text=result)
except ValueError as error:
showerror(title='Error', message=error)
def reset(self):
self.temperature_entry.delete(0, "end")
self.result_label.text = ''
class ControlFrame(ttk.LabelFrame):
def __init__(self, container):
super().__init__(container)
self['text'] = 'Options'
# radio buttons
self.selected_value = tk.IntVar()
ttk.Radiobutton(
self,
text='F to C',
value=0,
variable=self.selected_value,
command=self.change_frame).grid(column=0, row=0, padx=5, pady=5)
ttk.Radiobutton(
self,
text='C to F',
value=1,
variable=self.selected_value,
command=self.change_frame).grid(column=1, row=0, padx=5, pady=5)
self.grid(column=0, row=1, padx=5, pady=5, sticky='ew')
# initialize frames
self.frames = {}
self.frames[0] = ConverterFrame(
container,
'Fahrenheit',
TemperatureConverter.fahrenheit_to_celsius)
self.frames[1] = ConverterFrame(
container,
'Celsius',
TemperatureConverter.celsius_to_fahrenheit)
self.change_frame()
def change_frame(self):
frame = self.frames[self.selected_value.get()]
frame.reset()
frame.tkraise()
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title('Temperature Converter')
self.geometry('300x120')
self.resizable(False, False)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
ControlFrame(app)
app.mainloop()
Code language: Python (python)Summary #
- Use
tkraise()method to bring a frame on top a list of frames.