Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to manipulate various attributes of a Tkinter window.
The following simple program shows the main window:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
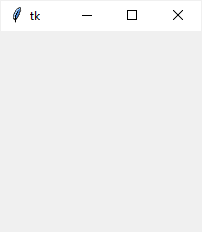
The main window has a title that defaults to tk. It also has three system buttons including Minimize, Maximize, and Close.
Let’s learn how to change the attributes of the main window.
Changing the window title #
To change the window’s title, you use the title() method like this:
root.title(new_title)Code language: Python (python)For example, the following changes the title of the root window to 'Tkinter Window Demo':
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
To get the current title of a window, you use the title() method with no argument:
title = root.title()Code language: Python (python)Changing window size and location #
In Tkinter, the position and size of a window on the screen is determined by its geometry.
The following shows the geometry specification:
widthxheight±x±yCode language: Python (python)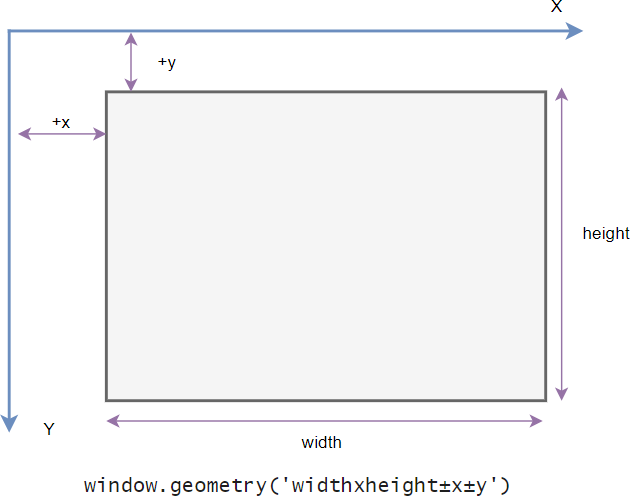
In this specification:
- The
widthrepresents the window’s width in pixels. - The
heightrepresents the window’s height in pixels. - The
xparameter denotes the window’s horizontal position. For example, a value of+50signifies the left edge of the window should be positioned 50 pixels from the left edge of the screen. Conversely, a value of-50indicates the right edge of the window should be 50 pixels from the right edge of the screen. - The
yparameter denotes the window’s vertical position. For example, a value of+50signifies the top edge of the window should be positioned 50 pixels below the top of the screen. Conversely, a value of-50indicates the bottom edge of the window should be 50 pixels above the bottom of the screen.
To change the size and position of a window, you use the geometry() method:
root.geometry(new_geometry)Code language: Python (python)The following example changes the size of the window to 600x400 and the position of the window to 50 pixels from the top and left of the screen:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.geometry('600x400+50+50')
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Sometimes, you may want to center the window on the screen. The following program illustrates how to do it:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window - Center')
window_width = 300
window_height = 200
# get the screen dimension
screen_width = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screen_height = root.winfo_screenheight()
# find the center point
center_x = int(screen_width/2 - window_width / 2)
center_y = int(screen_height/2 - window_height / 2)
# set the position of the window to the center of the screen
root.geometry(f'{window_width}x{window_height}+{center_x}+{center_y}')
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- First, get the screen width and height using the
winfo_screenwidth()andwinfo_screenheight()methods. - Second, calculate the center coordinate based on the screen and window’s width and height.
- Finally, set the geometry for the main window using the
geometry()method.
If you want to get the current geometry of a window, you can use the geometry() method without providing any argument:
root.geometry()Code language: Python (python)Resizing behavior #
By default, you can resize the width and height of a window. To prevent the window from resizing, you can use the resizable() method:
root.resizable(width,height)Code language: Python (python)The resizable() method has two parameters that specify whether the width and height of the window can be resizable.
The following shows how to make the window with a fixed size:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.geometry('600x400+50+50')
root.resizable(False, False)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
When a window is resizable, you can specify the minimum and maximum sizes using the minsize() and maxsize() methods:
window.minsize(min_width, min_height)
window.maxsize(max_width, max_height)Code language: Python (python)Transparency #
Tkinter allows you to specify the transparency of a window by setting its alpha channel ranging from 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque):
window.attributes('-alpha',0.5)Code language: Python (python)The following example illustrates a window with 50% transparent:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.geometry('600x400+50+50')
root.resizable(False, False)
root.attributes('-alpha', 0.5)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
Window stacking order #
The window stack order refers to the order of windows placed on the screen from bottom to top. The closer window is on the top of the stack and it overlaps the one lower.
To ensure that a window is always at the top of the stacking order, you can use the -topmost attribute like this:
window.attributes('-topmost', 1)Code language: Python (python)To move a window up or down of the stack, you can use the lift() and lower() methods:
window.lift()
window.lift(another_window)
window.lower()
window.lower(another_window)Code language: Python (python)The following example places the root window on top of all other windows. In other words, the root window is always on top:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.geometry('300x200+50+50')
root.resizable(0, 0)
root.attributes('-topmost', 1)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Changing the default icon #
Tkinter window displays a default icon. To change this default icon, you follow these steps:
- Prepare an image in the
.icoformat. If you have the image in other formats likepngorjpg, you can convert it to the.icoformat. There are many online tools that allow you to do it quite easily. - Place the icon in a folder that can be accessible from the program.
- Call the
iconbitmap()method of the window object. Theiconbitmap()method is primarily designed for Windows and require.icofiles.
The following program illustrates how to change the default icon to a new one (on Windows only).
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.geometry('300x200+50+50')
root.resizable(False, False)
# Ensure icon is in the assets folder relative to your script.
root.iconbitmap('./assets/pythontutorial.ico')
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
If you want to use the above icon, you can download it to your computer:
On Linux or macOS, you can use a PhotoImage and the iconphoto() method to show an icon as follows:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter Window Demo')
root.geometry('300x200+50+50')
root.resizable(False, False)
try:
# Use iconphoto on Linux and macOS
photo = tk.PhotoImage(file='./assets/python_icon.png') #.png or .gif
root.iconphoto(False, photo)
except tk.TclError:
print("icon file not found.")
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Note that you must use a .png or .gif file instead of an .ico file on Linux and macOS.
Summary #
- Use the
title()method to change the title of the window. - Use the
geometry()method to change the size and location of the window. - Use the
resizable()method to specify whether a window can be resizable horizontally or vertically. - Use the
window.attributes('-alpha',0.5)to set the transparency for the window. - Use the
window.attributes('-topmost', 1)to make the window always on top. - Use
lift()andlower()methods to move the window up and down of the window stacking order. - Use the
iconbitmap()method to change the default icon of the window.