Summary: In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use multiple threads in Tkinter applications to make them more responsive.
When to use Tkinter with Threads #
Let’s start with a simple program:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import time
def task():
# Simulate a long-running task
for i in range(5):
print(f"Task running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Task completed!")
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("300x100")
root.title("Tkinter Thread Example")
button = ttk.Button(root, text="Start Thread", command=task)
button.pack(pady=10)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)How it works.
First, define the task() function that takes 5 seconds to finish:
def task():
# Simulate a long-running task
for i in range(5):
print(f"Task running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Task completed!")Code language: Python (python)Second, create a main window with a button:
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("300x100")
root.title("Tkinter Thread Example")
button = ttk.Button(
root,
text="Start Thread",
command=task
)
button.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)When you click the button, the program executes the task function. During the function execution, the program freezes. It means that you cannot interact with the program by moving the window or clicking the button:
In Tkinter applications, the main loop should always start in the main thread. It handles events and updates the user interface (UI).
If you have an operation that takes time, you should execute it in a separate thread. To create and control multiple threads in Tkinter applications, you use the built-in threading module.
For more information on how to use the threading module, you can follow the Python threading tutorial.
The following program shows how to execute the task function in a separate thread:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import time
from threading import Thread
def task():
# Simulate a long-running task
for i in range(5):
print(f"Task running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Task completed!")
def handle_click():
t = Thread(target=task)
t.start()
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("300x100")
root.title("Tkinter Thread Example")
button = ttk.Button(
root,
text="Start Thread",
command=handle_click
)
button.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)How it works:
First, import the Thread class from the threading module:
from threading import ThreadCode language: Python (python)Second, define a function handle_click that creates a new thread and starts it:
def handle_click():
t = Thread(target=task)
t.start()Code language: Python (python)The new thread will execute the task function.
Third, bind the handle_click function to the command of the button:
button = ttk.Button(
root,
text="Start Thread",
command=handle_click
)Code language: Python (python)If you run the program and click the button, it will create two threads:
- The main thread is responsible for updating the user interface.
- A second thread executes the
taskfunction.
Since the task function does not block the main thread, you can interact with the program like moving main window. It does not freeze like before.
Getting values from threads #
To get value from a thread, you follow these steps:
First, define a new class that extends the Thread class and define additional attributes you want to access after the thread finishes:
class CustomThread(Thread):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.result = NoneCode language: Python (python)Second, override the run() method of the Thread class, execute a task, and update the result:
def run(self):
# execute a task
# update the result
self.result = return_valueCode language: Python (python)For example, the following program shows how to get a random number in a separate thread and display the result on the main window:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import time
from threading import Thread
import random
class RandomNumber(Thread):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.result = None
def run(self):
for i in range(3):
print(f"Thread running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Thread completed!")
self.result = random.randint(1, 100)
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry("400x130")
self.title("Tkinter Thread Example")
# Create a label to display the result
self.result_var = tk.StringVar()
self.label = ttk.Label(
self,
text="Result will appear here",
font=("TkDefaultFont", 24),
textvariable=self.result_var
)
self.label.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
# Create a button to start the thread
self.button = ttk.Button(
self,
text="Get a Random Number",
command=self.handle_click
)
self.button.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
def handle_click(self):
thread = RandomNumber()
thread.start()
self.monitor(thread)
def monitor(self, thread):
if thread.is_alive():
self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread))
else:
self.result_var.set(thread.result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)How it works.
First, define the RandomNumber class that extends the Thread class:
class RandomNumber(Thread):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.result = None
def run(self):
for i in range(3):
print(f"Thread running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Thread completed!")
self.result = random.randint(1, 100) Code language: Python (python)We use the sleep() function in the run method to simulate a long-running operation. The run method takes 3 seconds before returning a random number between 1 and 100. Once the thread completes, we assign the random number to the result attribute.
Second, define the App class that extends the Tk class:
class App(tk.Tk):Code language: Python (python)When you click the button, the handle_click method executes that:
- Start a new
RandomNumberthread. - Call the monitor method to check if the thread is still running.
The monitor method checks the thread every 100 milliseconds. If the thread is not alive, it updates the result_var with the result of the RandomNumber thread:
def monitor(self, thread):
if thread.is_alive():
self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread))
else:
self.result_var.set(thread.result)Code language: Python (python)Once the value of the result_var object changes, it automatically updates the label on the main window.
Enhancing UI #
You can click the button to start another thread when the thread is running. This is not what we want. To prevent users from clicking the button when the thread is running, we can enhance the user interface:
- Disable the button when the thread starts.
- Enable the button when the thread completes.
Additionally, we can change the label to indicate the program is running like ‘Processing…’.
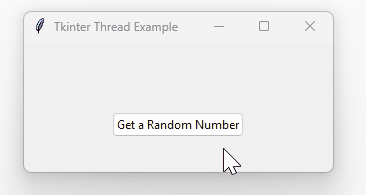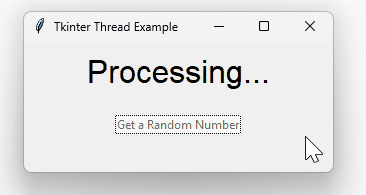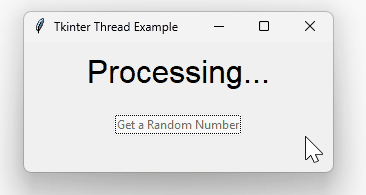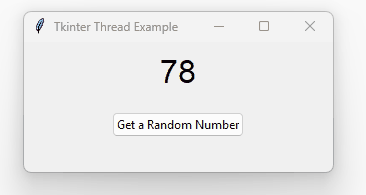
The following program illustrates these improvements:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import time
from threading import Thread
import random
class RandomNumber(Thread):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.result = None
def run(self):
for i in range(3):
print(f"Thread running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Thread completed!")
self.result = random.randint(1, 100)
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry("400x130")
self.title("Tkinter Thread Example")
# Create a label to display the result
self.result_var = tk.StringVar()
self.label = ttk.Label(
self,
text="Result will appear here",
font=("TkDefaultFont", 24),
textvariable=self.result_var
)
self.label.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
# Create a button to start the thread
self.button = ttk.Button(
self,
text="Get a Random Number",
command=self.handle_click
)
self.button.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
def handle_click(self):
# Disable the button to prevent multiple clicks
self.button.config(state=tk.DISABLED)
self.result_var.set("Processing...")
# Start the thread
thread = RandomNumber()
thread.start()
# Monitor the thread
self.monitor(thread)
def monitor(self, thread):
if thread.is_alive():
self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread))
else:
# Show the result
self.result_var.set(thread.result)
# Enable the button again
self.button.config(state=tk.NORMAL)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)First, disable the button and change the label to "Processing..." before starting a new thread:
def handle_click(self):
# Disable the button to prevent multiple clicks
self.button.config(state=tk.DISABLED)
self.result_var.set("Processing...")
# Start the thread
thread = RandomNumber()
thread.start()
# Monitor the thread
self.monitor(thread) Code language: Python (python)Second, enable the button when the thread completes:
def monitor(self, thread):
if thread.is_alive():
self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread))
else:
# Show the result
self.result_var.set(thread.result)
# Enable the button again
self.button.config(state=tk.NORMAL)Code language: Python (python)Adding a Progressbar #
We can improve the program by adding a Progressbar widget to it:
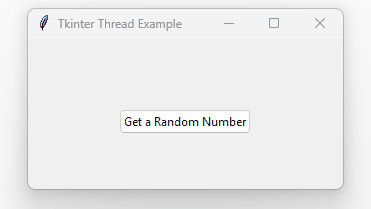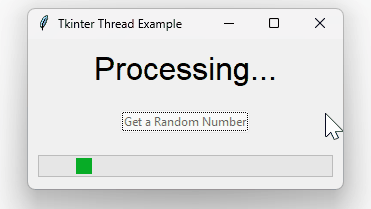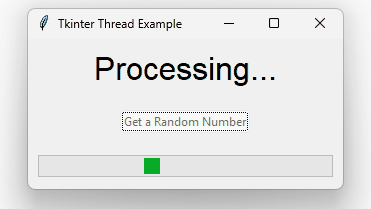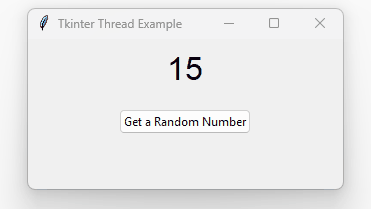
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import time
from threading import Thread
import random
class RandomNumber(Thread):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.result = None
def run(self):
for i in range(3):
print(f"Thread running... {i+1}/5")
time.sleep(1)
print("Thread completed!")
self.result = random.randint(1, 100)
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry("400x150")
self.title("Tkinter Thread Example")
# Create a label to display the result
self.result_var = tk.StringVar()
self.label = ttk.Label(
self,
text="Result will appear here",
font=("TkDefaultFont", 24),
textvariable=self.result_var
)
self.label.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
# Create a progress bar
self.progress_bar = ttk.Progressbar(self, mode='indeterminate')
# Create a button to start the thread
self.button = ttk.Button(
self,
text="Get a Random Number",
command=self.handle_click
)
self.button.pack(padx=10 ,pady=10)
def handle_click(self):
# Disable the button to prevent multiple clicks
self.button.config(state=tk.DISABLED)
self.result_var.set("Processing...")
# Show the progress bar
self.progress_bar.pack(padx=10, pady=10, fill=tk.X, expand=True)
self.progress_bar.start()
self.result_var.set("Processing...")
# Start the thread
thread = RandomNumber()
thread.start()
# Monitor the thread
self.monitor(thread)
def monitor(self, thread):
if thread.is_alive():
self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread))
else:
# Hide the progress bar
self.progress_bar.stop()
self.progress_bar.pack_forget()
# Enable the button again
self.button.config(state=tk.NORMAL)
# Display the result
self.result_var.set(thread.result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)How it works.
First, create a Progressbar widget in the __init__ method of the App class:
self.progress_bar = ttk.Progressbar(self, mode='indeterminate')Code language: Python (python)Second, show the Progressbar widget and start it in the handle_click button method before starting a new thread:
self.progress_bar.pack(padx=10, pady=10, fill=tk.X, expand=True)
self.progress_bar.start()Code language: Python (python)Third, stop the Progressbar and hide it after the thread completes in the monitor() method:
self.progress_bar.stop()
self.progress_bar.pack_forget()Code language: Python (python)Summary #
- Execute long-running tasks in separate threads to make Tkinter programs responsive.