Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to change the Tkinter theme from one to another.
Introduction to Tkinter ttk themes #
In Tkinter, a theme determines the “look & feel” of all the widgets. It’s a collection of styles for all the ttk widgets.
A style specifies the appearance of a widget class e.g., a Button. Each theme comes with a set of styles. It’s possible to change the appearance of widgets by:
- Modifying the built-in styles
- or creatting new styles
Tkinter allows you to change the current theme to another. When you change the current theme to a new one, Tkinter will apply the styles of that theme to all the ttk widgets.
To get the available themes, you use the theme_names() method of the ttk.Style instance.
First, create a new instance of the ttk.Style class:
style = ttk.Style(root)Code language: Python (python)Second, get the available themes by calling the theme_names() method:
style.theme_names()Code language: Python (python)To get the current theme, you use the theme_use() method:
current_theme = style.theme_use()Code language: Python (python)Note that every operating system (OS) such as Windows, macOS, and Linux comes with its own predefined themes. If you use the theme_names() and theme_use() methods on different OS, you’ll get different results.
To change the current theme to a new one, you pass the new theme name to the theme_use() method:
style.theme_use(theme_name)Code language: Python (python)The following program shows all themes in your system and allows you to change one theme to another:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# root window
self.title('Theme Demo')
self.geometry('400x300')
self.style = ttk.Style(self)
# label
label = ttk.Label(self, text='Name:')
label.grid(column=0, row=0, padx=10, pady=10, sticky='w')
# entry
textbox = ttk.Entry(self)
textbox.grid(column=1, row=0, padx=10, pady=10, sticky='w')
# button
btn = ttk.Button(self, text='Show')
btn.grid(column=2, row=0, padx=10, pady=10, sticky='w')
# radio button
self.selected_theme = tk.StringVar()
theme_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(self, text='Themes')
theme_frame.grid(padx=10, pady=10, ipadx=20, ipady=20, sticky='w')
for theme_name in self.style.theme_names():
rb = ttk.Radiobutton(
theme_frame,
text=theme_name,
value=theme_name,
variable=self.selected_theme,
command=self.change_theme)
rb.pack(expand=True, fill='both')
def change_theme(self):
self.style.theme_use(self.selected_theme.get())
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()
Code language: Python (python)In this example, when you select a theme from the radio button list, the change_theme() method will apply the selected theme.
If you run the program on Windows 10, you’ll see the following window:
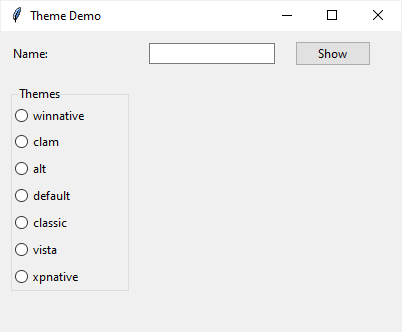
If you change the theme to classic, you’ll see the style of the widgets (Label, Entry, Button, LabelFrame, and Radio Button) change to the following:
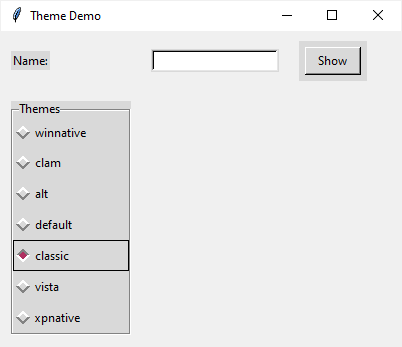
Summary #
- Create an instance of the
ttk.Styleclass to access the style database. - Use the
style.theme_names()method to get available themes from the Operating System on which the Tkinter application is running. - Use the
style.theme_use()method to change the current theme to a new one.