Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Tkinter StringVar object and how to use it to manipulate values of widgets.
Introduction to the Tkinter StringVar #
The Tkinter StringVar helps you manage the value of a widget such as a Label or Entry more effectively.
To create a new StringVar object, you use the StringVar constructor like this:
string_var = tk.StringVar(master, value, name)Code language: Python (python)The StringVar constructor accepts three optional arguments:
masteris a widget that theStringVarobject associated with. If you skip themaster, it defaults to the main window.valueis the initial value that defaults to an empty string''.nameis a Tcl name that defaults toPY_VARnumwhere num is 1, 2, 3, etc., for examplePY_VAR1,PY_VAR2.
After creating the StringVar object, you can assign it to the textvariable of a widget that accepts a StringVar object. For example, the following assigns the string_var to textvariable of the Entry widget:
entry = ttk.Entry(master, textvariable=string_var)Code language: Python (python)To get the current value of the Entry widget, you can use the get() method of the StringVar object:
string_var.get()Code language: Python (python)The StringVar object will notify you whenever its value changes. This feature is useful if you want to automatically update other widgets based on the current value of the StringVar object.
To invoke a callback whenever the value of an StringVar object changes, you use the trace_add() method of the StringVar object:
string_var.trace_add(mode, callback)Code language: Python (python)The trace_add method defines a trace callback for the StringVar. It accepts two variables:
modedetermines when the StringVar should call the callback. The mode can be a string ‘write’, ‘read’, or ‘unset’, or a tuple of these strings. For example, if you set the mode to ‘write, the StringVar will call the callback whenever its values changes.callbackis the function that the StringVar will call according to themode.
If you don’t want to trace the value of a StringVar object, you can use the trace_remove() method:
string_var.trace_remove(mode, callback)Code language: CSS (css)The trace_remove() method has two parameters mode and callback that has the same meaning as the ones in the trace_add() method.
Tkinter StringVar example #
The following example illustrates how to link the StringVar object with an Entry widget:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Tkinter StringVar')
root.geometry("250x100")
pack_attr = {'anchor': tk.W, 'padx': 5, 'pady': 5, 'fill': tk.X}
ttk.Label(root, text='Name').pack(**pack_attr)
# Entry
name_var = tk.StringVar()
name_entry = ttk.Entry(root, textvariable=name_var)
name_entry.pack(**pack_attr)
name_entry.focus()
output_label = ttk.Label(root, textvariable=name_var)
output_label.pack(**pack_attr)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
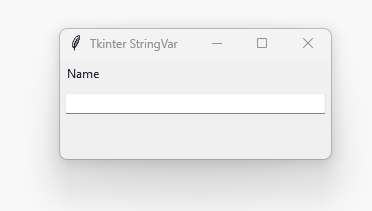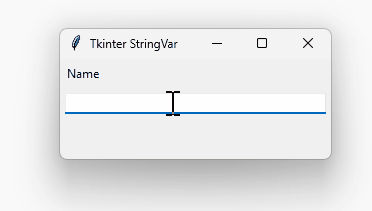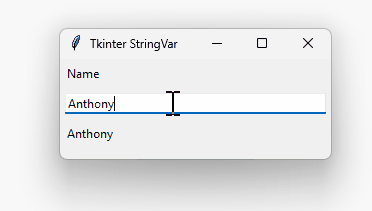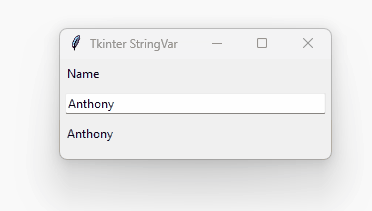
How it works.
First, create a new StringVar object:
name_var = tk.StringVar()Code language: Python (python)Second, link the StringVar object with an Entry widget:
name_entry = ttk.Entry(frame, textvariable=name_var)Code language: Python (python)Third, link the same StringVar object with a Label widget:
output_label = ttk.Label(output_frame, textvariable=name_var)Code language: Python (python)Tracing text changes example #
The following example illustrates how to use the StringVar object to trace text changes.
The root window has two Entry widgets:
- password
- password confirmation
If you confirm the wrong password, the program shows an error message. Otherwise, it’ll show a success message:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Change Password')
root.geometry("300x200")
ERROR = 'Error.TLabel'
WARNING = 'Warning.TLabel'
SUCCESS = 'Success.TLabel'
style = ttk.Style(root)
style.configure('Error.TLabel', foreground='red')
style.configure('Success.TLabel', foreground='green')
style.configure('Warning.TLabel', foreground='orange')
def validate_password(*args):
password = password_var.get()
confirm_password = password_confirmation_var.get()
if not password or not confirm_password:
set_message("", WARNING)
return
if confirm_password == password:
set_message(
"The passwords match!", SUCCESS)
return
if password.startswith(confirm_password):
set_message('The passwords are partially matching!', WARNING)
return
set_message("The passwords don't match!", ERROR)
def set_message( message, message_type=None):
output_label['text'] = message
if message_type is not None:
output_label['style'] = message_type
pack_attr = {'anchor': tk.W, 'padx': 5, 'pady': 5, 'fill': tk.X}
output_label = ttk.Label(root, text='')
output_label.pack(**pack_attr)
# password field
ttk.Label(root, text='New Password:').pack(**pack_attr)
password_var = tk.StringVar()
password = ttk.Entry(root, textvariable=password_var, show='*')
password.pack(**pack_attr)
password.focus()
# password confirmation field
ttk.Label(root, text='Password Confirmation:').pack(**pack_attr)
password_confirmation_var = tk.StringVar()
password_confirmation = ttk.Entry(root, textvariable=password_confirmation_var, show='*')
password_confirmation.pack(**pack_attr)
password_confirmation_var.trace_add('write', validate_password)
# button
button = ttk.Button(
root,
text='Change Password'
)
button.pack(anchor=tk.W, padx=5, pady=5)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
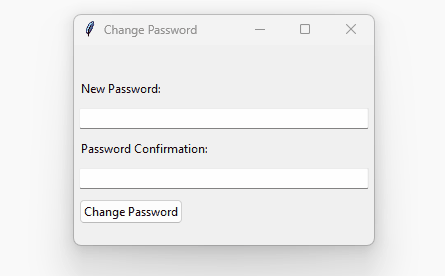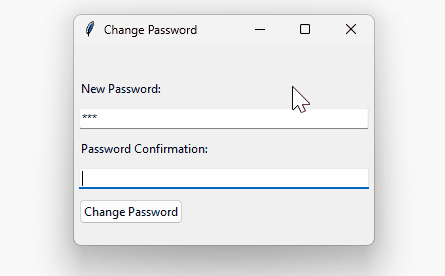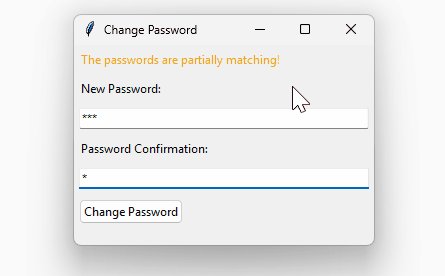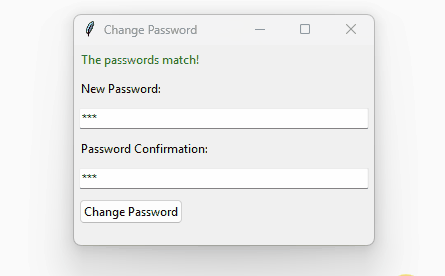
How it works:
First, define two constants ERROR and SUCCESS that will be set to the message_label based on the result of the validation:
ERROR = 'Error.TLabel'
SUCCESS = 'Success.TLabel'
WARNING = 'Warning.TLabel'Code language: Python (python)Second, create two StringVar objects:
password_var = tk.StringVar()
password_confirmation_var = tk.StringVar()Code language: Python (python)Third, use the trace_add() method to call the validate() function whenever the text of the password confirmation widget changes:
password_confirmation_var.trace_add('write', validate_password)Code language: Python (python)Finally, show the success message if the passwords match in the validate() method. Otherwise, show a warning message if the password starts with the confirmed password. If the passwords don’t match, show an error message.
Summary #
- Use Tkinter
StringVarobject to track and change the string state of a widget.