Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create Tkinter Spinbox widgets.
Introduction to the Tkinter Spinbox widget #
A Spinbox widget allows you to select a value from a set of values, which can include a range of numbers.
A Spinbox has an area for displaying the current value and a pair of arrowheads.
When you click the upward-pointing arrowhead, the Spinbox advances to the next higher value in the sequence.
If the current value reaches the maximum, you can set it to the minimum.
On the other hand, if you click the downward-pointing arrowhead, the Spinbox decreases the current value to the next lower value in the sequence.
If the current value reaches the lowest, you can set it to the maximum.
Additionally, you can directly enter a value into the Spinbox widget as you would with an Entry widget.
To create a Spinbox widget, you use the ttk.Spinbox constructor:
ttk.Spinbox(master, from_, to, textvariable, wrap)Code language: CSS (css)In this syntax:
- The
masteris the parent widget of theSpinboxwidget. - The
from_is the minimum value. Becausefromis the Python keyword, it has to be suffixed with the underscore(_) to avoid the compilation error. - The
tovalue represents the maximum value. - The
textvariablespecifies aStringVarorIntVarobject of the Tkinter class that holds the current value of theSpinbox. - The
wrapis a Boolean value. Ifwrapis set toTrue, when the current value reaches the maximum value, it’s set to the lowest value if you click the upward-pointing arrowhead and vice versa. Ifwrapset toFalse, the widget sets the current value to the maximum if you click the downward-pointing arrowhead.
Note that the ttk.Spinbox has been available since Python 3.7. If you are using a lower version, you need to use the tk.Spinbox.
Getting the current value #
To get the current value of the Spinbox, you can access the textvariable. For example:
current_value = tk.StringVar(value=0)
spin_box = ttk.Spinbox(
container,
from_=0,
to=30,
textvariable=current_value,
wrap=True)Code language: PHP (php)In this example, the current_value holds the current value of the Spinbox widget. You can obtain it by calling the get() method:
current_value.get()Code language: CSS (css)Also, you can use the get() method of the Spinbox object:
spin_box.get()Code language: CSS (css)Executing a function #
To execute a function when the value of the Spinbox changes, you can assign that function to the command option. For example:
def value_changed():
print(current_value.get())
current_value = tk.StringVar(value=0)
spin_box = ttk.Spinbox(
container,
from_=0,
to=30,
textvariable=current_value,
command=value_changed) Code language: Python (python)In this example, the value_changed function will execute automatically whenever the value of the Spinbox changes.
Setting discrete steps #
To set a list of discrete steps for a Spinbox, you assign a tuple of discrete numbers to the values option like this:
ttk.Spinbox(
...
values=tuple
...
) Tkinter Spinbox widget examples #
Let’s take some examples of creating a Spinbox widget.
1) A simple Tkinter Spinbox widget example #
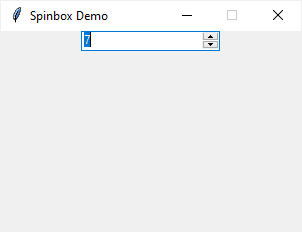
The following program illustrates how to use the Spinbox:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# root window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('300x200')
root.resizable(False, False)
root.title('Spinbox Demo')
# Spinbox
current_value = tk.StringVar(value=0)
spin_box = ttk.Spinbox(
root,
from_=0,
to=30,
textvariable=current_value,
wrap=True)
spin_box.pack()
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
2) Tkinter Spinbox with discrete steps #
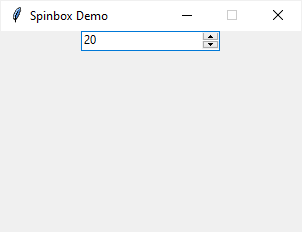
The following example shows how to create a Spinbox with discrete steps:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# root window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('300x200')
root.resizable(False, False)
root.title('Spinbox Demo')
# spinbox
current_value = tk.StringVar()
spin_box = ttk.Spinbox(
root,
from_=0,
to=50,
values=(0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50),
textvariable=current_value,
wrap=True)
spin_box.pack()
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
Summary #
- Use
ttk.Spinbox(container, **options)to create a Spinbox. - Set
wrap=Trueto set the current value to the minimum value when it reaches the maximum value and vice versa.