Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the Tkinter PanedWindow widget to divide the space of a frame or a window.
Introduction to the Tkinter PanedWindow widget #
The PaneWindow widget divides the space of a frame or a window. A PaneWindow is like a Frame that acts as a container for holding child widgets
Typically, a PanedWindow contains a vertical or horizontal stack of child widgets:
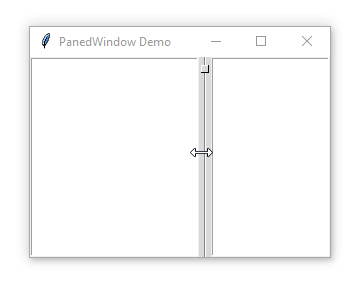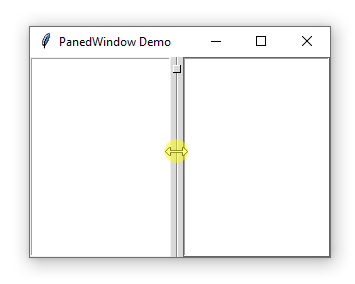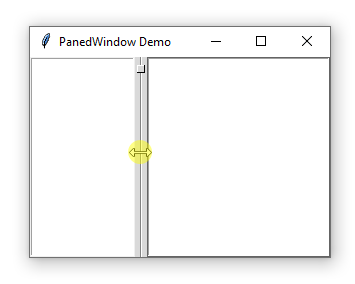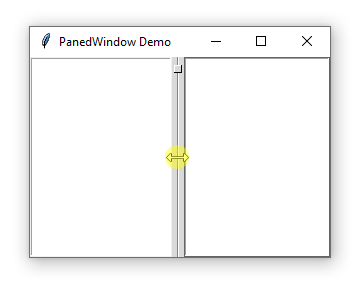
A PanedWindow uses a bar to separate the child widgets. This bar is called a sash.
A sash can have a handle which is a small square that you can drag it with a mouse:
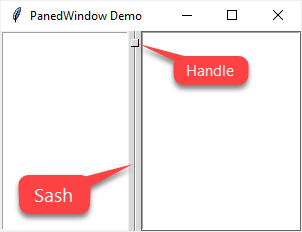
A pane is an area occupied by one child widget.
To create a PanedWindow widget, you use the following syntax:
ttk.PanedWindow(container, **options)Code language: CSS (css)A notable option of a PanedWindow widget is the orient option.
If you set the orient to tk.HORIZONTAL, it’ll stack child widgets side by side. If orient is tk.VERTICAL, it’ll stack child widgets top to bottom. The orient option defaults to tk.VERTICAL.
Tkinter PanedWindow widget example #
The following example illustrates how to use the PanedWindow widget to separate two Listbox widgets:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('PanedWindow Demo')
root.geometry('300x200')
# change style to classic (Windows only)
# to show the sash and handle
style = ttk.Style()
style.theme_use('classic')
# paned window
pw = ttk.PanedWindow(orient=tk.HORIZONTAL)
# Left listbox
left_list = tk.Listbox(root)
left_list.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
pw.add(left_list)
# Right listbox
right_list = tk.Listbox(root)
right_list.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
pw.add(right_list)
# place the panedwindow on the root window
pw.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
root.mainloop()Code language: PHP (php)Output:
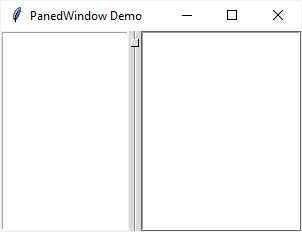
If you run the program on Windows, you’re likely will not see the sash and handle displaying. To make it visible, you can set the default theme to classic
Summary #
- Use the Tkinter
PanedWindowwidget to divide the space of a window or a frame.