Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Python float() to convert a number or a string to a floating point number.
Introduction to the Python float() #
The float() accepts a string or an number, either an integer or a floating-point number, and converts it to a floating-point number, if possible:
float(x)Code language: Python (python)If x is a string, it should contain a decimal number. Also, it can have an optional sign like a minus (-) or plus (+).
If x is an integer or a floating point number, the float()float()OverflowError.
If x is an object, the float()x.__ method. If the object x does not have the float__float__() method, the float()__index__() method.
The x parameter is optional. If you omit it, the float() will return 0.0.
Python float() examples #
Let’s take some examples of using the Python float().
1) Using float() to convert a string to a floating point number #
The following example uses the float() to convert strings to floating point numbers:
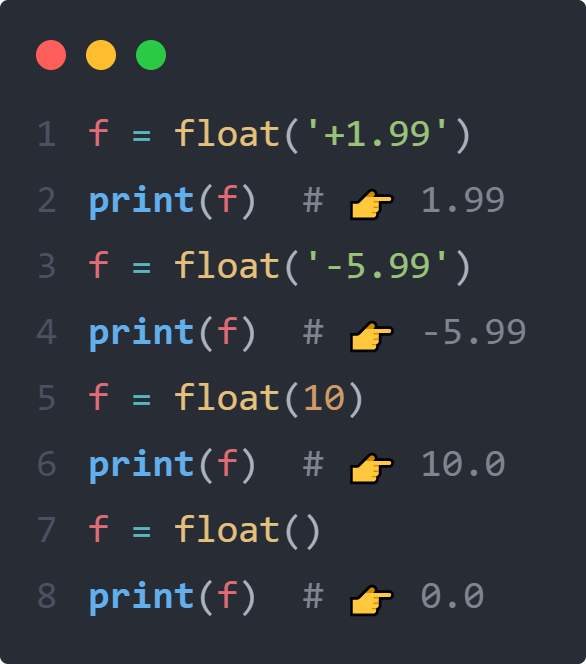
f = float('+1.99')
print(f) # 👉 1.99
f = float('-5.99')
print(f) # 👉 -5.99
f = float('199e-001')
print(f) # 👉 19.9
f = float('+1E3')
print(f) # 👉 1000.0
f = float('-Infinity')
print(f) # 👉 -infCode language: Python (python)2) Using float() to convert an integer to a floating point number #
The following example uses the float() to convert integers to floating point numbers:
f = float(10)
print(f) # 👉 10.0
f = float(-20)
print(f) # 👉 -20.0
f = float(0)
print(f) # 👉 0.0
f = float()
print(f) # 👉 0.0Code language: Python (python)3) Using the Python float() to convert an object to a floating point number #
The following example illustrates how to convert an object to a floating point number:
class Product:
def __init__(self, name, price):
self.name = name
self.price = price
def __float__(self):
return float(self.price)
phone = Product('phone', 999)
print(float(phone))Code language: Python (python)Output:
999.0Code language: Python (python)How it works.
First, define a class Product that has two attributes name and price. The __float__() method returns the floating point number of the price:
class Product:
def __init__(self, name, price):
self.name = name
self.price = price
def __float__(self):
return float(self.price)Code language: Python (python)Second, create a new instance of the product and convert it to a floating point number:
phone = Product('phone', 999)
print(float(phone))Code language: Python (python)Summary #
- Use the Python
float()to convert a string or an integer to a floating point number.