Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to read a CSV file in Python using the built-in csv module.
What is a CSV file #
CSV stands for comma-separated values. A CSV file is a delimited text file that uses a comma to separate values.
A CSV file consists of one or more lines. Each line is a data record. And each data record consists of one or more values separated by commas. In addition, all the lines of a CSV file have the same number of values.
Typically, you use a CSV file to store tabular data in plain text. The CSV file format is quite popular and supported by many software applications such as Microsoft Excel and Google Spreadsheet.
Reading a csv file in Python #
To read a CSV file in Python, you follow these steps:
First, import the csv module:
import csvCode language: Python (python)Second, open the CSV file using the built-in open() function in the read mode:
f = open('path/to/csv_file')Code language: Python (python)If the CSV contains UTF8 characters, you need to specify the encoding like this:
f = open('path/to/csv_file', encoding='UTF8')Code language: Python (python)Third, pass the file object (f) to the reader() function of the csv module. The reader() function returns a csv reader object:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)Code language: Python (python)The csv_reader is an iterable object of lines from the CSV file. Therefore, you can iterate over the lines of the CSV file using a for loop:
for line in csv_reader:
print(line)Code language: Python (python)Each line is a list of values. To access each value, you use the square bracket notation []. The first value has an index of 0. The second value has an index of 1, and so on.
For example, the following accesses the first value of a particular line:
line[0]Code language: Python (python)Finally, always close the file once you’re no longer access it by calling the close() method of the file object:
f.close() Code language: Python (python)It’ll be easier to use the with statement so that you don’t need to explicitly call the close() method.
The following illustrates all the steps for reading a CSV file:
import csv
with open('path/to/csv_file', 'r') as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
for line in csv_reader:
# process each line
print(line)
Code language: Python (python)Reading a CSV file examples #
We’ll use the country.csv file that contains country information including name, area, 2-letter country code, 3-letter country code:
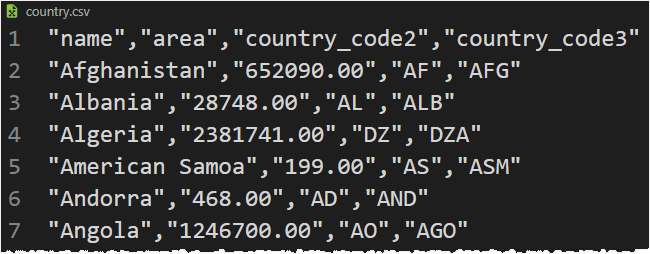
The following shows how to read the country.csv file and display each line to the screen:
import csv
with open('country.csv', encoding="utf8") as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
for line in csv_reader:
print(line)Code language: Python (python)Output:
['name', 'area', 'country_code2', 'country_code3']
['Afghanistan', '652090.00', 'AF', 'AFG']
['Albania', '28748.00', 'AL', 'ALB']
['Algeria', '2381741.00', 'DZ', 'DZA']
['American Samoa', '199.00', 'AS', 'ASM']
...
Code language: Python (python)The country.csv has the first line as the header. To separate the header and data, you use the enumerate() function to get the index of each line:
import csv
with open('country.csv', encoding="utf8") as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
for line_no, line in enumerate(csv_reader, 1):
if line_no == 1:
print('Header:')
print(line) # header
print('Data:')
else:
print(line) # data
Code language: Python (python)In this example, we use the enumerate() function and specify the index of the first line as 1.
Inside the loop, if the line_no is 1, the line is the header. Otherwise, it’s a data line.
Another way to skip the header is to use the next() function. The next() function forwards to the reader to the next line. For example:
import csv
with open('country.csv', encoding="utf8") as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
# skip the first row
next(csv_reader)
# show the data
for line in csv_reader:
print(line)
Code language: Python (python)The following reads the country.csv file and calculate the total areas of all countries:
import csv
total_area = 0
# calculate the total area of all countries
with open('country.csv', encoding="utf8") as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
# skip the header
next(csv_reader)
# calculate total
for line in csv_reader:
total_area += float(line[1])
print(total_area)Code language: Python (python)Output:
148956306.9Code language: Python (python)Reading a CSV file using the DictReader class #
When you use the csv.reader() function, you can access values of the CSV file using the bracket notation such as line[0], line[1], and so on. However, using the csv.reader() function has two main limitations:
- First, the way to access the values from the CSV file is not so obvious. For example, the
line[0]implicitly means the country name. It would be more expressive if you can access the country name likeline['country_name']. - Second, when the order of columns from the CSV file is changed or new columns are added, you need to modify the code to get the right data.
This is where the DictReader class comes into play. The DictReader class also comes from the csv module.
The DictReader class allows you to create an object like a regular CSV reader. But it maps the information of each line to a dictionary (dict) whose keys are specified by the values of the first line.
By using the DictReader class, you can access values in the country.csv file like line['name'], line['area'], line['country_code2'], and line['country_code3'].
The following example uses the DictReader class to read the country.csv file:
import csv
with open('country.csv', encoding="utf8") as f:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(f)
# skip the header
next(csv_reader)
# show the data
for line in csv_reader:
print(f"The area of {line['name']} is {line['area']} km2")
Code language: Python (python)Output:
The area of Afghanistan is 652090.00 km2
The area of Albania is 28748.00 km2
The area of Algeria is 2381741.00 km2
...
Code language: Python (python)If you want to have different field names other than the ones specified in the first line, you can explicitly specify them by passing a list of field names to the DictReader() constructor like this:
import csv
fieldnames = ['country_name', 'area', 'code2', 'code3']
with open('country.csv', encoding="utf8") as f:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(f, fieldnames)
next(csv_reader)
for line in csv_reader:
print(f"The area of {line['country_name']} is {line['area']} km2")
Code language: Python (python)In this example, instead of using values from the first line as the field names, we explicitly pass a list of field names to the DictReader constructor.
Summary #
- Use
csv.reader()function orcsv.DictReaderclass to read data from a CSV file.