Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the PyQt QVBoxLayout to arrange widgets vertically.
Introduction to the PyQt QVBoxLayout #
The QVBoxLayout divides the parent widget into vertical boxes and places the child widgets sequentially from top to bottom.
This program illustrates how to use the QVBoxLayout class:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons and add them to the layout
titles = ['Find Next', 'Find All', 'Close']
buttons = [QPushButton(title) for title in titles]
for button in buttons:
layout.addWidget(button)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Output:
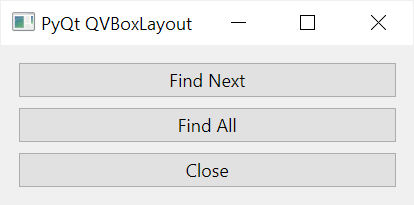
How it works.
First, create a QVBoxLayout object:
layout = QVBoxLayout()Code language: Python (python)Next, set the layout for the MainWindow by calling its setLayout() method:
self.setLayout(layout)Code language: Python (python)Then, define a list of three strings that represent button titles:
titles = ['Find Next', 'Find All', 'Close']Code language: JavaScript (javascript)After that, create three buttons (QPushButton) from the list titles using a list comprehension:
buttons = [QPushButton(title) for title in titles]Finally, add the buttons to the layout using a for loop:
for button in buttons:
layout.addWidget(button)Code language: Python (python)Alignments #
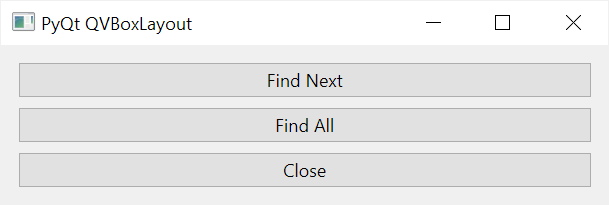
The QVBoxLayout stretches each widget type in a specific way. For example, the QVBoxLayout stretches the QPushButton horizontally, not vertically.
It means that when you increase the width of the parent widget, the widths of all the buttons also increase:
However, when you increase the height of the parent widget, the heights of the buttons don’t change. More importantly, the QVBoxLayout allocates evenly the spaces of the parent widget to each button:
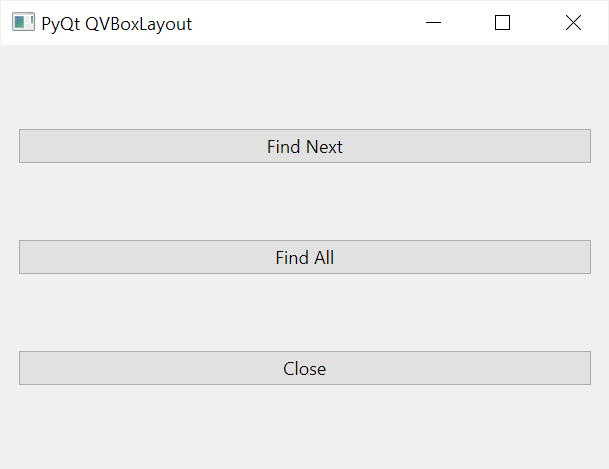
When the parent widget has more space for the child widgets, you can align the child widgets within the parent widget using vertical spacers.
Align bottom #
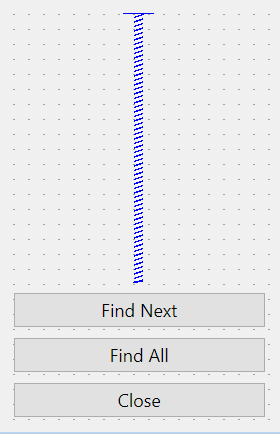
To push the buttons to the bottom of the parent widget, you add a vertical spacer at the beginning of the layout by using the addStretch() method of the QVBoxLayout object:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# add a spacer
layout.addStretch()
# create buttons and add them to the layout
titles = ['Find Next', 'Find All', 'Close']
buttons = [QPushButton(title) for title in titles]
for button in buttons:
layout.addWidget(button)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)If you increase the height of the window, the vertical spacer will stretch to the end of the QVBoxLayout and leaves enough spaces for the buttons:
Align top #
Similarly, you can add a vertical spacer as the last item of the layout to push the buttons to the top by calling the addStretch() method after adding the buttons to the layout:
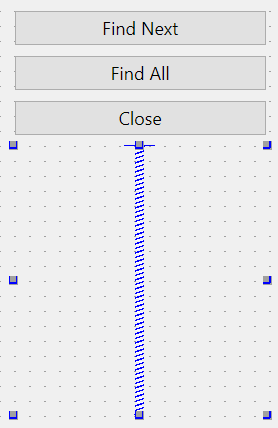
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons and add them to the layout
titles = ['Find Next', 'Find All', 'Close']
buttons = [QPushButton(title) for title in titles]
for button in buttons:
layout.addWidget(button)
# add a spacer
layout.addStretch()
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Align center #
To align the buttons in the center of the parent widget, you add a vertical spacer at the beginning and one at the end of the layout like this:
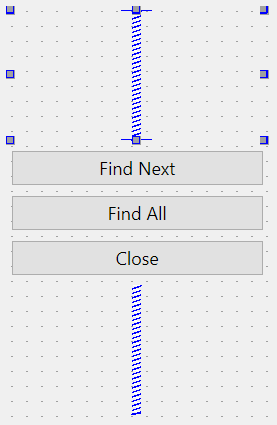
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# add a spacer
layout.addStretch()
# create buttons and add them to the layout
titles = ['Find Next', 'Find All', 'Close']
buttons = [QPushButton(title) for title in titles]
for button in buttons:
layout.addWidget(button)
# add a spacer
layout.addStretch()
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Note that you can add a vertical spacer between the widgets in the QVBoxLayout. For example, the following adds a vertical spacer between the second and third buttons:

import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons
find_next_btn = QPushButton('Find Next')
find_all_btn = QPushButton('Find All')
close_btn = QPushButton('Find All')
# add the first & second buttons to the layout
layout.addWidget(find_next_btn)
layout.addWidget(find_all_btn)
# add a spacer
layout.addStretch()
# add the third button
layout.addWidget(close_btn)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Setting layout stretch factors #
The following program displays three QLabel widgets with different background colors red, green, and blue using the QVBoxLayout:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons
label_1 = QLabel()
label_1.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:red}')
label_2 = QLabel()
label_2.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:green}')
label_3 = QLabel()
label_3.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:blue}')
layout.addWidget(label_1)
layout.addWidget(label_2)
layout.addWidget(label_3)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())Code language: Python (python)Note that we use the style sheets to set the background color for the QLabel widgets.
Unlike QPushButton widgets, the QLabel widgets stretch both vertically and horizontally when you resize the parent widget:
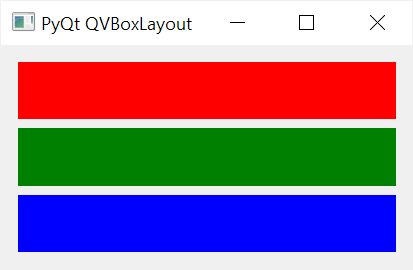
To allocate spaces for each QLabel widget proportionally, you use the setStretchFactor() method with the following syntax:
setStretchFactor(widget, factor)Code language: Python (python)The setStretchFactor() method sets a stretch factor for the widget to stretch within the layout. Therefore, you need to setStretchFactor() method after adding the child widgets to the layout.
The following program uses the setStretchFactor() method to set the stretch factors for the first, second, and third QLabel widgets as 1, 2, and 3:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons
label_1 = QLabel('')
label_1.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:red}')
label_2 = QLabel('')
label_2.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:green}')
label_3 = QLabel('')
label_3.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:blue}')
layout.addWidget(label_1)
layout.addWidget(label_2)
layout.addWidget(label_3)
layout.setStretchFactor(label_1, 1)
layout.setStretchFactor(label_2, 2)
layout.setStretchFactor(label_3, 3)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)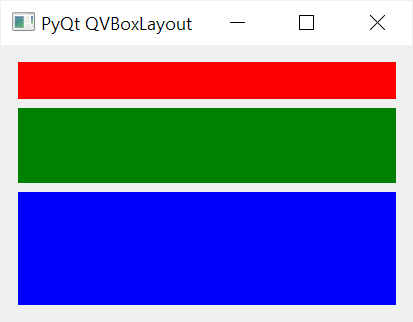
Because of the stretch factors, the second QLabel widget takes twice as much space as the first one and the third QLabel widget uses space that is three times bigger than the first one.
Setting spaces between widgets #
By default, the QVBoxLayout sets a default space between widgets. To change the spaces between widgets, you use the setSpacing() method.
The following example uses the setSpacing() method to set the spaces between QLabel widgets to zero:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons
label_1 = QLabel('')
label_1.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:red}')
label_2 = QLabel('')
label_2.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:green}')
label_3 = QLabel('')
label_3.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:blue}')
layout.addWidget(label_1)
layout.addWidget(label_2)
layout.addWidget(label_3)
layout.setSpacing(0)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Output:
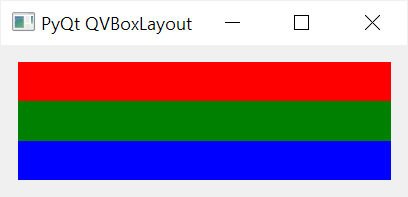
Setting content margins #
By default, the QVBoxLayout sets specific left, top, right, and bottom margins for a widget. To change the margins, you use the setContentsMargins() method:
setContentsMargins(self, left: int, top: int, right: int, bottom: int) -> NoneCode language: PHP (php)For example, the following uses the setContentsMargins() method to set the margins for QLabel widgets to zero:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QVBoxLayout
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QVBoxLayout')
# create a layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create buttons
label_1 = QLabel('')
label_1.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:red}')
label_2 = QLabel('')
label_2.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:green}')
label_3 = QLabel('')
label_3.setStyleSheet('QLabel{background-color:blue}')
layout.addWidget(label_1)
layout.addWidget(label_2)
layout.addWidget(label_3)
# set the contents margins
layout.setContentsMargins(0, 0, 0, 0)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Output:
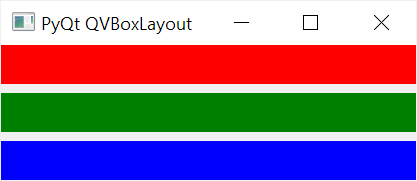
Summary #
- Use PyQt
QVBoxLayoutto divide the parent widget into vertical boxes and place the child widgets sequentially from top to bottom. - Use the
addStretch()method of theQVBoxLayoutobject to add a vertical spacer to the layout to align widgets at the top, bottom, or center. - Use the
setStretchFactor()method of theQVBoxLayoutobject to set a stretch factor for a widget in the layout. - Use the
setSpacing()method of theQVBoxLayoutobject to set the spaces between child widgets. - Use the
setContentsMargins()method of theQVBoxLayoutobject to set the left, top, right, and bottom margins of the contents.