Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the PyQt QSlider class to create a slider widget.
Introduction to the PyQt QSlider #
A slider is a widget for controlling a bounded value. A slider allows you to move a handle along a horizontal or vertical groove. A slider translates the position of the handle into an integer within a valid range.
To create a slider, you use the PyQt QSlider class:
QSlider(orientation[, parent=None])Code language: Python (python)The QSlider accepts two arguments:
Orientationspecifies the orientation of the slider. The valid values areQt.Orientation.VerticalandQt.Orientation.Horizontal.Parentis the parent widget of the slider.
For example, the following creates a horizontal slider:
slider = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal, self)Code language: Python (python)Output:

And the following creates a vertical slider:
slider = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Vertical, self)Code language: Python (python)Output:

Range #
To set the range of values for the slider, you use the setRange() method:
slider.setRange(min,max)Code language: Python (python)Also, you can set the setMinimum() or setMaximum() methods:
slider.setMinimum(min)
slider.setMaximum(max)Code language: Python (python)Single step #
When you press the up/down or left/right arrow key, the handle of the slider will increment/decrement a single step.
To set the single step, you use the setSingleStep() method:
slider.setSingleStep(step)Code language: Python (python)Page step #
If you press the page up / page down key, the handle of the slider will increment/decrement a page step. To set a page step, you use the setPageStep() method:
slider.setPageStep(pageStep)Code language: Python (python)Setting the current value #
To set a value for the slider, you use the setValue() method:
slider.setValue(value)Code language: Python (python)The value() method returns the current value of the slider:
current_value = slider.value()Code language: Python (python)Displaying tick marks #
By default, a slider doesn’t have tick marks. To show the tick marks, you use the set method. The TickPosition()setTickPosition sets the TickPosition property to a value.
The horizontal slider has two options:
The QSlider.TicksAbove – shows tick marks above the slider:
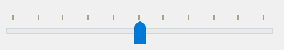
The QSlider.TicksBelow – shows tick marks below the slider.
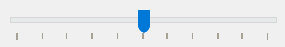
The vertical slider also has two options:
The QSlider.TicksLeft – shows the tick marks on the left of the slider:
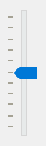
The QSlider.TicksRight – shows the tick marks on the right of the slider:
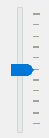
The QSlider.TicksBothSides shows the tick marks on both sides of the groove:
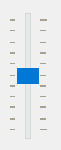
By default, the TickPosition is QSlider.NoTicks that do not display any tick marks.
Setting interval #
To set the interval between tick marks, you use the setTickInteral() method. By default, the ticket interval is zero.
If the tick interval is zero, the slider will choose between singleStep and pageStep.
Signals #
The QSlider has some signals but the most important one is valueChanged. The QSlider emits the valueChanged signal whenever the value of the slider changes.
PyQt QSlider example #
The following program uses the QSlider class to create a slider. A label displays the current value of the slider.
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QSlider, QLabel, QFormLayout
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QSlider')
self.setMinimumWidth(200)
# create a grid layout
layout = QFormLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
slider = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal, self)
slider.setRange(0, 100)
slider.setValue(50)
slider.setSingleStep(5)
slider.setPageStep(10)
slider.setTickPosition(QSlider.TickPosition.TicksAbove)
slider.valueChanged.connect(self.update)
self.result_label = QLabel('', self)
layout.addRow(slider)
layout.addRow(self.result_label)
# show the window
self.show()
def update(self, value):
self.result_label.setText(f'Current Value: {value}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())Code language: Python (python)Output:
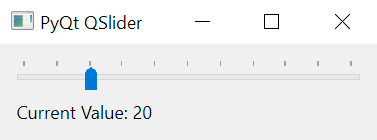
How it works.
First, create a QSlider object:
slider = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal, self)Code language: Python (python)Next, set the range, value, single step, page step, and tick position:
slider.setRange(0, 100)
slider.setValue(50)
slider.setSingleStep(10)
slider.setPageStep(20)
slider.setTickPosition(QSlider.TickPosition.TicksAbove)Code language: Python (python)Then, connect to the valueChanged() signal to the update() method:
slider.valueChanged.connect(self.update)Code language: Python (python)After that, create a QLabel object that will display the current value of the slider whenever the slider’s value changes:
self.result_label = QLabel('', self)Code language: Python (python)Finally, define the update() method that changes the text of the QLabel to the current value of the slider:
def update(self, value):
self.result_label.setText(f'Current Value: {value}')Code language: Python (python)Summary #
- Use the PyQt
QSliderwidget to create a slider. - Connect to the
valueChangedsignal to update the slider’s value.