Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the PyQt QMessageBox class to create a modal dialog that alerts the user or asks the user to make a decision.
Introduction to PyQt QMessageBox class #
The QMessageBox class allows you to create a modal dialog that alerts the user with important information or asks the user a question and receives an answer.
The QMessageBox provides some useful static methods for displaying a message box:
information()– show an information message.question()– ask the user a question and receives an answer.warning()– show a warning message.critical()– display critical information.
PyQt QMessageBox examples #
The following program shows a window with four buttons, clicking a button will display a corresponding message:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMessageBox, QWidget, QHBoxLayout, QPushButton
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('PyQt QMessageBox')
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 100)
layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
btn_question = QPushButton('Question')
btn_question.clicked.connect(self.question)
btn_info = QPushButton('Information')
btn_info.clicked.connect(self.info)
btn_warning = QPushButton('Warning')
btn_warning.clicked.connect(self.warning)
btn_critical = QPushButton('Critical')
btn_critical.clicked.connect(self.critical)
layout.addWidget(btn_question)
layout.addWidget(btn_info)
layout.addWidget(btn_warning)
layout.addWidget(btn_critical)
self.show()
def info(self):
QMessageBox.information(
self,
'Information',
'This is important information.'
)
def warning(self):
QMessageBox.warning(
self,
'Warning',
'This is a warning message.'
)
def critical(self):
QMessageBox.critical(
self,
'Critical',
'This is a critical message.'
)
def question(self):
answer = QMessageBox.question(
self,
'Confirmation',
'Do you want to quit?',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes |
QMessageBox.StandardButton.No
)
if answer == QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes:
QMessageBox.information(
self,
'Information',
'You selected Yes. The program will be terminated.',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Ok
)
self.close()
else:
QMessageBox.information(
self,
'Information',
'You selected No.',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Ok
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())Code language: Python (python)How it works.
The question() method displays a message box with a question that asks the user to select either a Yes or No button:
answer = QMessageBox.question(
self,
'Confirmation',
'Do you want to quit?',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes |
QMessageBox.StandardButton.No
)Code language: Python (python)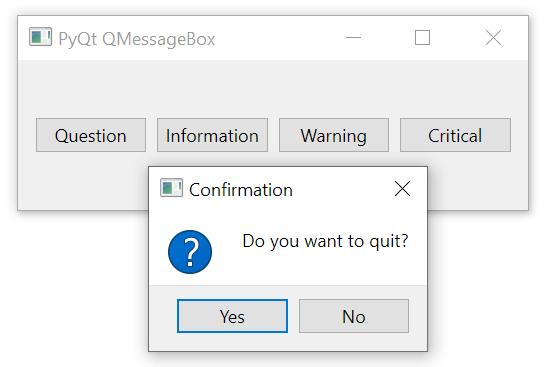
To get which button the user clicked, you compare the return value of the question() method with the Yes and No members of the QMessageBox.StandardButton enum:
if answer == QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes:
QMessageBox.information(
self,
'Information',
'You selected Yes. The program will be terminated.',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Ok
)
self.close()
else:
QMessageBox.information(
self,
'Information',
'You selected No.',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Ok
)Code language: Python (python)The information() method displays a message box with information. It accepts the parent widget, the title of the message box, and the message.
QMessageBox.information(
self,
'Information',
'This is important information.'
)Code language: Python (python)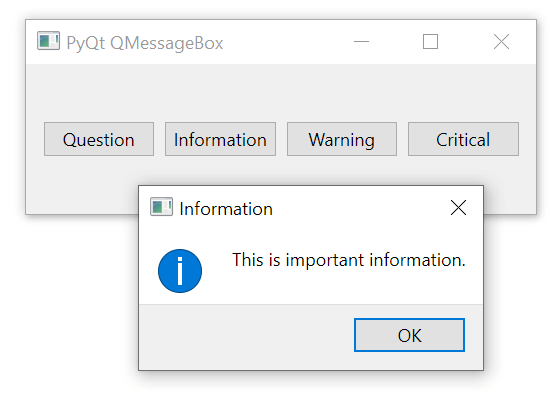
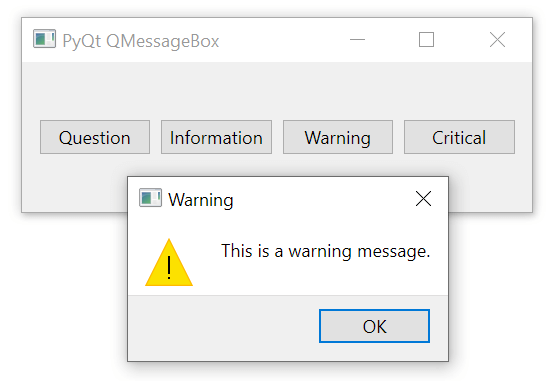
The warning() method displays a warning message. Its appearance is like the information except for the warning icon:
QMessageBox.warning(
self,
'Warning',
'This is a warning message.'
)Code language: Python (python)Output:
The critical() method displays a critical message on the message box. The stop icon makes the message critical.
QMessageBox.critical(
self,
'Critical',
'This is a critical message.'
)Code language: Python (python)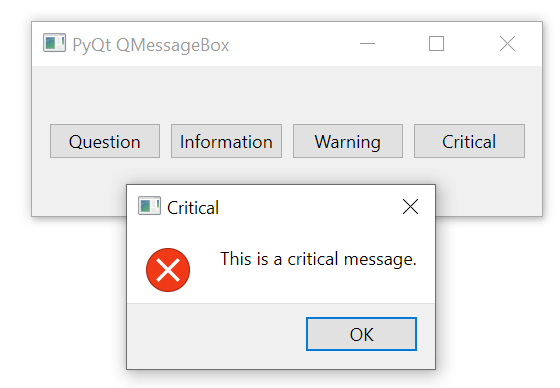
Summary #
- Use
QMessageBoxclass to create a modal dialog that displays a message box or asks the user a question and receives an answer.