Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the PyQt QMainWindow to create the main window of an application.
Introduction to the PyQt QMainWindow #
So far, you have learned how to use QWidgetQWidget
PyQt provides you with QMainWindowQWidget class, you can create the main window by inheriting it from the QMainWindow
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):Code language: Python (python)PyQt divides the QMainWindow widget into some sections as shown in the following picture:
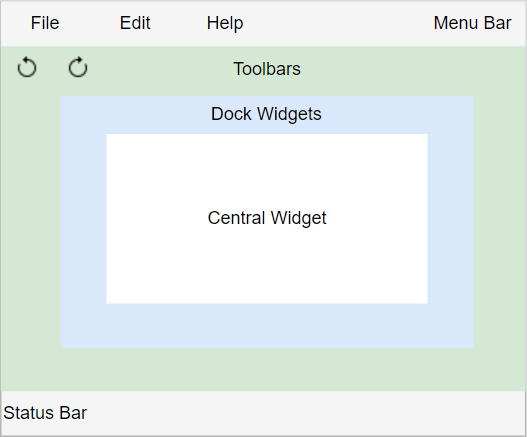
Note that you should not set a layout for the QMainWindow. If you do so, you’ll break the preset arrangement of the widgets.
Set the central widget #
A QMainWindowsetCentralWidget() method of the QMainWindow
For example, the following uses the setCentralWidget() method to set the QTextEdit as the central widget:
self.setCentralWidget(QTextEdit())Code language: Python (python)Set the window title #
To set the title for the main window, you use the setWindowTitle() method. For example:
self.setWindowTitle('Editor')Code language: PHP (php)Set the window icon #
To set the icon for the window, you use the setWindowIcon() method. For example:
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('./assets/editor.png'))Code language: PHP (php)In this example:
- First, create a
QIconand pass in the image path./assets/editor.png - Second, pass the
QIconobject to thesetWindowIcon()method to set the icon for the window.
Set the geometry for the main window #
The geometry defines the coordinate of the window (x,y) or (top, left) and the window’s width and height:
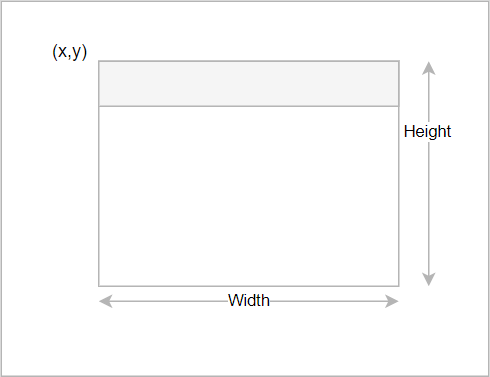
To set the geometry for the window, you use the setGeometry() method of the QMainWindow object. For example, the following uses the setGeometry() method to set the geometry for the window:
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 500, 300)Code language: CSS (css)In this example, the window will appear at (100, 100) with a width of 500px and height of 300px:
The following program creates the main window using the QMainWindow, sets the central widget, and the window’s title, icon, and geometry:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTextEdit, QToolBar, QStatusBar
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('Editor')
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('./assets/editor.png'))
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 500, 300)
self.text_edit = QTextEdit(self)
self.setCentralWidget(self.text_edit)
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Adding a menu bar #
To add a menu bar to the main window, you use the menuBar() method of the QMainWindow:
menu_bar = self.menuBar()Code language: Python (python)The menuBar()QMenuBarQMenuBarmenuBar()QMenuBarQMenuBar
By default, the menu bar is empty. To add a menu to a menu bar, you use the addMenu() method. For example, the following adds three submenus File, Edit, and Help:
file_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&File')
edit_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Edit')
help_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Help')Code language: Python (python)The addMenu()QMenu object that represents a drop-down submenu. The string that we pass to the addMenu()
The character & will underscore the character of the menu label when you press the ALT key. For example, &File will underscore the letter F.

Action #
To add menu items to a menu, you need to create actions. An action is an object of the QAction class that represents the functionality of the application.
An action object requires a name and a callback to function properly. In addition, an action may contain an icon and a keyboard shortcut.
To create an action, you can call the addAction() method of a QMenu. For example, the following adds three actions to the File menu:
file_menu.addAction('New', lambda: self.text_edit.clear())
file_menu.addAction('Open', lambda: print('Open'))
file_menu.addAction('Exit', self.destroy)Code language: PHP (php)If you click the New menu item, the QTextEdit widget will clear all contents. Similarly, by clicking the Open menu item, you’ll see a message on the console, and clicking the Exit menu will end the program.
Also, you can create a QAction object and connects its triggered signal to a slot. For example, the following creates undo and redo actions and adds them to the Edit menu:
undo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/undo.png'), 'Undo', self)
undo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Z')
undo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.undo)
edit_menu.addAction(undo_action)
redo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/redo.png'), 'Redo', self)
redo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Y')
redo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.redo)
edit_menu.addAction(redo_action)Code language: Python (python)Note that the undo and redo actions have icons and keyboard shortcuts.
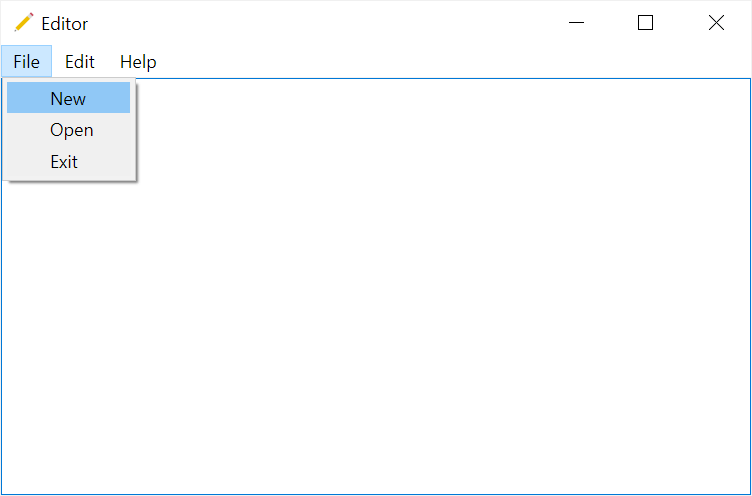
The following program shows how to add a menu bar and menu items to the File and Edit menus:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTextEdit, QToolBar, QStatusBar
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('Editor')
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('./assets/editor.png'))
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 500, 300)
self.text_edit = QTextEdit(self)
self.setCentralWidget(self.text_edit)
# setting menu
menu_bar = self.menuBar()
file_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&File')
edit_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Edit')
help_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Help')
file_menu.addAction('New', lambda: self.text_edit.clear())
file_menu.addAction('Open', lambda: print('Open'))
file_menu.addAction('Exit', self.destroy)
undo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/undo.png'), 'Undo', self)
undo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Z')
undo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.undo)
edit_menu.addAction(undo_action)
redo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/redo.png'), 'Redo', self)
redo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Y')
redo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.redo)
edit_menu.addAction(redo_action)
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Output:
Adding a toolbar #
A toolbar is a bar of icons and/or text that expose the most commonly used function of the application. To add a toolbar to the application:
- First, create a new
QToolBarobject. - Second, add the toolbar to the application using the
addToolbar()method of theQMainWindow.
For example, the following creates a new toolbar and adds it to the application:
toolbar = QToolBar('Main toolbar')
self.addToolBar(toolbar)Code language: Python (python)To add an item to the toolbar, you use the addAction() method of the QToolBar object. For example:
toolbar.addAction(undo_action)
toolbar.addAction(redo_action)Code language: Python (python)The following program shows add a toolbar with the undo and redo actions:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTextEdit, QToolBar
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('Editor')
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('./assets/editor.png'))
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 500, 300)
self.text_edit = QTextEdit(self)
self.setCentralWidget(self.text_edit)
# setting menu
menu_bar = self.menuBar()
file_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&File')
edit_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Edit')
help_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Help')
file_menu.addAction('New', lambda: self.text_edit.clear())
file_menu.addAction('Open', lambda: print('Open'))
file_menu.addAction('Exit', self.destroy)
undo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/undo.png'), 'Undo', self)
undo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Z')
undo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.undo)
edit_menu.addAction(undo_action)
redo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/redo.png'), 'Redo', self)
redo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Y')
redo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.redo)
edit_menu.addAction(redo_action)
# adding a toolbar
toolbar = QToolBar('Main toolbar')
self.addToolBar(toolbar)
toolbar.addAction(undo_action)
toolbar.addAction(redo_action)
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())Code language: Python (python)Adding a status bar #
A status bar is a bar located at the bottom of the main window. Typically, a status bar displays short text messages and/or informational widgets.
To add a status bar to the application, you create a QStatusBar object and set it to the main window using the setStatusBar() method:
status_bar = QStatusBar()
self.setStatusBar(status_bar)Code language: Python (python)The statusBar() method of the QMainWindow returns a QStatusBarQStatusBar
To display a short message, you use the showMessage() method of the QStatusBar object:
status_bar.showMessage('Awesome Editor v1.0')Code language: Python (python)Or you can directly use the QStatusBar object returned by the statusBar() method of the main window:
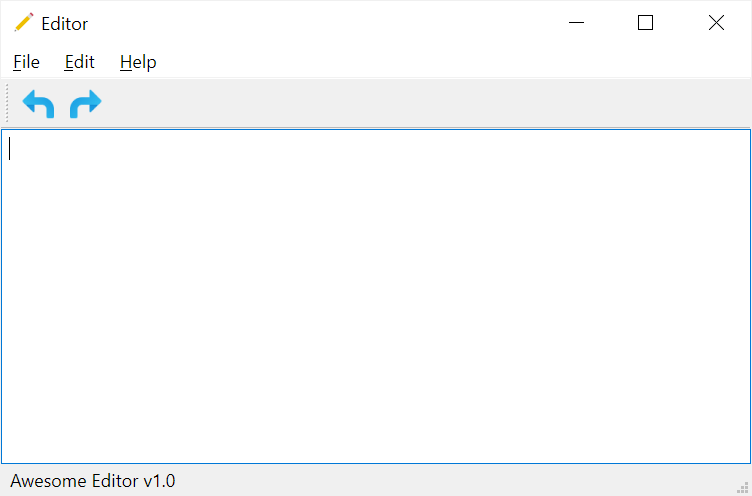
self.status_bar.showMessage('Awesome Editor v1.0')Code language: Python (python)The following program shows a status bar:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTextEdit, QToolBar, QStatusBar
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('Editor')
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('./assets/editor.png'))
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 500, 300)
self.text_edit = QTextEdit(self)
self.setCentralWidget(self.text_edit)
# setting menu
menu_bar = self.menuBar()
file_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&File')
edit_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Edit')
help_menu = menu_bar.addMenu('&Help')
file_menu.addAction('New', lambda: self.text_edit.clear())
file_menu.addAction('Open', lambda: print('Open'))
file_menu.addAction('Exit', self.destroy)
undo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/undo.png'), 'Undo', self)
undo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Z')
undo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.undo)
edit_menu.addAction(undo_action)
redo_action = QAction(QIcon('./assets/redo.png'), 'Redo', self)
redo_action.setShortcut('Ctrl+Y')
redo_action.triggered.connect(self.text_edit.redo)
edit_menu.addAction(redo_action)
# adding a toolbar
toolbar = QToolBar('Main toolbar')
self.addToolBar(toolbar)
toolbar.addAction(undo_action)
toolbar.addAction(redo_action)
# status bar
self.status_bar = QStatusBar()
self.setStatusBar(self.status_bar)
self.status_bar.showMessage('Awesome Editor v1.0')
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Output:
Summary #
- Use the
QMainWindowclass to create the main window for the application. - Use the
setWindowTitle()method to set the title. - use the
setWindowIcon()method to set the window’s icon. - Use the
setGeometry()method to set the window’s geometry including the (top, left) coordinates, width, and height. - Use the
menuBar()method to add a menu bar to the main window. - use the setToolBar() method to set a toolbar for the main window.
- Use the
statusBar()method to add a status bar to the main window.