Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use build a simple API that returns a list of todos and a detail of a todo using Django only.
Creating a virtual environment #
First, create a new directory called django_rest_api:
mkdir django_rest_apiSecond, navigate to the django_rest_api directory:
cd django_rest_apiCode language: Python (python)Third, create a virtual environment using the built-in venv module:
python -m venv venvCode language: Python (python)Fourth, activate the virtual environment:
venv/scripts/activateFifth, install the django package using pip command:
pip install djangoCode language: Python (python)Finally, create the requirements.txt file:
pip freeze > requirements.txtCode language: Python (python)Creating a new Django project #
First, create a new Django project called todolist:
django-admin startproject todolistSecond, navigate to the project directory:
cd todolistCode language: Python (python)Creating a new Django app #
First, create a new app called todo inside the todolist project:
django-admin startapp todoCode language: Python (python)Second, register the todo app in the settings.py of the todolist project
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'todo.apps.TodoConfig',
]Code language: Python (python)Defining the Todo model #
First, define the Todo model in the models.py of the todo app:
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class Todo(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
completed = models.BooleanField(default=False)
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
def __str__(self):
return self.titleCode language: Python (python)The Todo model has three fields: title, completed, and user.
The user references the User model of the django package, which specifies the account that created the todo.
Second, register the Todo model to the admin site by modifying the code in the admin.py in the todo app:
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Todo
admin.site.register(Todo)Code language: Python (python)By doing this, you can manage the todo on the Django admin site.
Making migrations & migrate models #
First, make a new migration:
python manage.py makemigrationsCode language: Python (python)Second, migrate the migrations to sync the models to the database:
python manage.py migrateCode language: Python (python)Third, create a super admin user to sign in to Django’s admin site:
python manage.py createsuperuserCode language: Python (python)Let’s call the user john.
Finally, start the Django development server:
python manage.py runserverCode language: Python (python)Creating some todos #
First, log in to the admin site via the URL http://localhost:8000/admin using the superuser john created above:
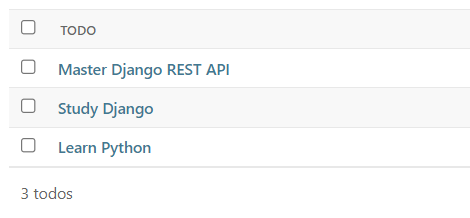
And add some todos:
Building an API with Django #
We’ll build an API with Django only. The API will have two endpoints:
todos/returns all todos.todos/idreturns the information of a specific todo specified by id. For example,todos/1returns the information of the todo with id 1.
First, create two view functions inside the views.py of the todo app:
from django.http import JsonResponse
from django.core.exceptions import ObjectDoesNotExist
from .models import Todo
def todo_list(request):
""" Return all todos
"""
# get all todos
todos = Todo.objects.all()
# prepare data to return
data = {'todos': list(todos.values())}
# return JSON
return JsonResponse(data)
def todo_detail(request, pk):
""" Return a todo instance
"""
try:
# find todo by id
todo = Todo.objects.get(pk=pk)
except ObjectDoesNotExist:
# return 404 if the todo does not exists
return JsonResponse({
'status_code': 404,
'error': f'Todo with id {pk} not found.'
})
else:
# prepare data to return
data = {
'id': todo.id,
'title': todo.title,
'completed': todo.completed,
'user': todo.user.username,
}
# return JSON
return JsonResponse(data)Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- The
todo_list()function gets all todos as a queryset, format it as a dictionary, and returns a JSON response using theJSONResponseobject. - The
todo_detail()function gets a todo by id and returns a JSON response with 404 if the todo doesn’t exist. Otherwise, it returns the detail of a todo model including username information.
Second, create urls.py inside the todo app and include it in the urls.py of the project:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include('todo.urls')), # new
]Code language: Python (python)The urls.py maps the API endpoints with the function views:
from django.urls import path
from .views import todo_list, todo_detail
urlpatterns = [
path('todos/', todo_list, name='todo-list'),
path('todos/<int:pk>', todo_detail, name='todo-detail'),
]Code language: Python (python)Third, open the http://localhost:8000/todos/ endpoint on the web browser, you’ll see three todos in JSON format:
{
"todos": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Learn Python",
"completed": false,
"user_id": 1
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Study Django",
"completed": false,
"user_id": 1
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Master Django REST API",
"completed": false,
"user_id": 1
}
]
}Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)Fourth, open the endpoint of the todo id 1 http://localhost:8000/todos/1, and you’ll see the following JSON response:
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Learn Python",
"completed": false,
"user": "john"
}Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)Finally, if you open an endpoint that doesn’t exist e.g., http://localhost:8000/todos/10, you’ll get a 404 error:
{
"status_code": 404,
"error": "Todo with id 10 not found."
}Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)As you can see, Django is capable of building API. But it requires a lot of effort for serializing Django’s model instances into JSON and vice versa.
Also, if you want to add more features to API like pagination, rate limiting, token authentication, etc. Django doesn’t provide all of these features out of the box.
This is why Django REST Framework comes into play. We’ll learn how to develop a fully RESTful API using the Django REST Framework in the next tutorials.
Download the project source code #
Click the following link to download the project source code:
Download the Django REST API project
Summary #
- Django is capable of building APIs but requires a lot of effort since it doesn’t provide API features out of the box.
- Use a third-party package like Django Rest Framework to build APIs efficiently.