Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to add extra fields to the ManyToManyField using the through argument.
In a many-to-many relationship, multiple rows in a table are associated with multiple rows in another table. To establish a many-to-many relationship, relational databases use a third table called the join table and create two one-to-many relationships from the source tables.
Typically, the join table contains the id values of the source tables so that rows in one table can relate to the rows in the other table.
Sometimes, you may want to add extra fields to the join table. For example, each employee may have multiple jobs during his/her career.
To track when an employee takes a job, you can add the begin_date and end_date fields to the join table.
To do that in Django, you use the ManyToManyField with the through argument.
For example, the following shows how to associate an employee with multiple jobs through the assignments:
class Employee(models.Model):
# ...
class Job(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
employees = models.ManyToManyField(Employee, through='Assignment')
def __str__(self):
return self.title
class Assignment(models.Model):
employee = models.ForeignKey(Employee, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
position = models.ForeignKey(Job, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
begin_date = models.DateField()
end_date = models.DateField(default=date(9999, 12, 31))Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- First, define the
Jobmodel, add theemployeesattribute that uses theManyToManyField, and passAssignmentas thethroughargument. - Second, define the
Assignmentclass that has two foreign keys, one links to theEmployeemodel, and the other links to theJobmodel. Also, add thebegin_dateandend_dateattributes to theAssignmentmodel.
Run the makemigrations to make new migrations:
python manage.py makemigrationsCode language: Python (python)Output:
Migrations for 'hr':
hr\migrations\0005_assignment_job_assignment_job.py
- Create model Assignment
- Create model Job
- Add field job to assignmentCode language: Python (python)And execute the migrate command to apply the changes to the database:
python manage.py migrateCode language: Python (python)Output:
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, hr, sessions
Running migrations:
Applying hr.0005_assignment_job_assignment_job... OKCode language: Python (python)Behind the scenes, Django creates the hr_job and hr_assignment tables in the database:
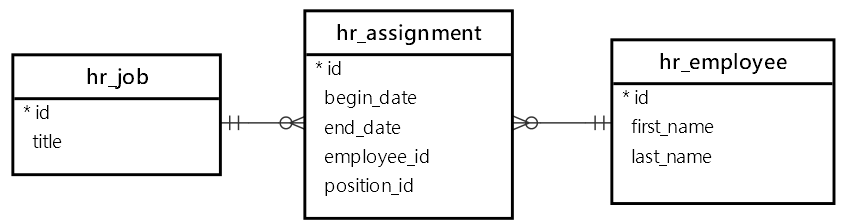
The hr_assignment is the join table. Besides the employee_id and position_id fields, it has the begin_date and end_date fields.
Creating new jobs #
First, run the shell_plus command:
python manage.py shell_plusCode language: Python (python)Second, create three new positions:
>>> j1 = Job(title='Software Engineer I')
>>> j1.save()
>>> j2 = Job(title='Software Engineer II')
>>> j2.save()
>>> j3 = Job(title='Software Engineer III')
>>> j3.save()
>>> Job.objects.all()
<QuerySet [<Job: Software Engineer I>, <Job: Software Engineer II>, <Job: Software Engineer III>]>Code language: Python (python)Creating instances for the intermediate models #
First, find the employee with the name John Doe and Jane Doe:
>>> e1 = Employee.objects.filter(first_name='John',last_name='Doe').first()
>>> e1
<Employee: John Doe>
>>> e2 = Employee.objects.filter(first_name='Jane', last_name='Doe').first()
>>> e2
<Employee: Jane Doe>Code language: Python (python)Second, create instances of the intermediate model (Assignment):
>>> from datetime import date
>>> a1 = Assignment(employee=e1,job=j1, begin_date=date(2019,1,1), end_date=date(2021,12,31))
>>> a1.save()
>>> a2 = Assignment(employee=e1,job=j2, begin_date=date(2022,1,1))
>>> a2.save()
>>> a3 = Assignment(employee=e2, job=j1, begin_date=date(2019, 3, 1))
>>> a3.save()Code language: Python (python)Third, find the employees that hold the Software Engineer I position (p1):
>>> j1.employees.all()
<QuerySet [<Employee: John Doe>, <Employee: Jane Doe>]>Code language: Python (python)Behind the scenes, Django executes the following query:
SELECT
"hr_employee"."id",
"hr_employee"."first_name",
"hr_employee"."last_name",
"hr_employee"."contact_id",
"hr_employee"."department_id"
FROM "hr_employee"
INNER JOIN "hr_assignment"
ON ("hr_employee"."id" = "hr_assignment"."employee_id")
WHERE "hr_assignment"."job_id" = 1Code language: Python (python)Similarly, you can find all employees that hold the Software Engineer II position:
>>> j2.employees.all()
<QuerySet [<Employee: John Doe>]>Code language: Python (python)Removing instances of the intermediate model instances #
First, remove Jane Doe (e2) from the Software Engineer II job using the remove() method:
>>> j2.employees.remove(e2) Code language: Python (python)Second, remove all employees from Software Engineer I job using the clear() method:
>>> j1.employees.clear() Code language: Python (python)The j1 job should not have any employees now:
>>> j1.employees.all()
<QuerySet []>Code language: CSS (css)Summary #
- Use the
throughargument in theManyToManyFieldto add extra fields to the many-to-many relationship.