Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll have a deep understanding of the Python bool class and how to handle boolean values effectively.
Introduction to the Python bool class #
To represent boolean values including True and False, Python uses the built-in bool class.
The bool class is the subclass of the int class. It means that the bool class inherits all properties and methods of the int class. In addition, the bool class has specific behaviors related to boolean operations.
If you use the issubclass() function for the bool and int classes, it’ll return True as follows:
is_child_class = issubclass(bool, int)
print(is_child_class)Code language: Python (python)Output:
TrueCode language: PHP (php)In fact, True and False are singleton objects of the bool class.
isinstance(True, bool)
isinstance(False, bool)Code language: Python (python)Output:
The following uses the isinstance() function to check if True and False are the instances of bool class:
True
True Code language: Python (python)Since both True and False are also int objects, you can convert them to integers:
true_value = int(True)
print(true_value)
false_value = int(False)
print(false_value)Code language: Python (python)Output:
1
0Code language: Python (python)Python interprets True as 1 and False as 0.
Please note that True and 1 are not the same object. Likewise, False and 0 are not the same.
Comparing boolean values #
Since True and False are singleton objects that always reference the same objects in the memory throughout the program.
Therefore, you can use either is or == operator to compare boolean values. The results are the same. For example:
a = True
b = True
print(a == b)
print(a is b)Code language: Python (python)Output:
True
True Code language: PHP (php)The same is applied to the False object:
a = False
b = False
print(a == b)
print(a is b)Code language: Python (python)Output:
True
True Code language: PHP (php)How Python bool() constructor works under the hood #
The Boolean constructor bool() accepts an object and returns True or False.
In Python, a class always contains a definition of how its instances evaluate to True and False. In other words, every object can be either True or False.
All objects have a boolean value of True, except the following objects:
NoneFalse0in any numeric type such as integer, float, and decimal.- Empty sequences e.g., list, tuple, string.
- Empty mapping types e.g., dictionary, set.
- Custom classes that implement
__bool__()or__len__()methods that returnFalseor0.
…which have a boolean value of False
The __bool__() method #
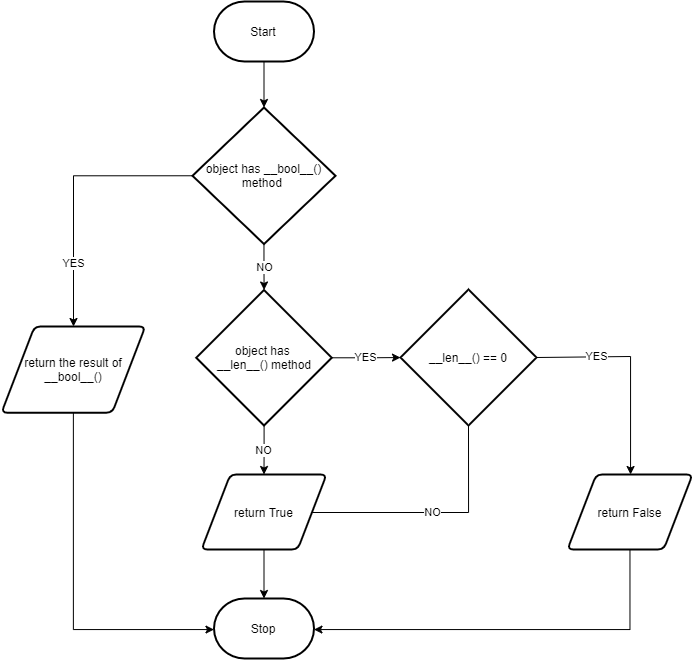
When you pass an object to the bool() constructor, Python returns the value of the __bool__() method of that object.
For example, the following shows the __bool__() method of the int class:
def __bool__(self):
return self != 0Code language: Python (python)When you call:
bool(200)Code language: Python (python)…Python actually executes:
200.__bool__()Code language: Python (python)…and therefore returns the result of 200 != 0, which is True.
However, if you call:
bool(0)Code language: Python (python)…Python executes:
0.__bool__()Code language: Python (python)…and therefore returns the result of 0 != 0, which is False.
The __len__() method #
If the class of the object doesn’t have the __bool__() method, Python will return the result of __len__() method.
If the result of the __len__() method is zero, the bool() returns False. Otherwise, it returns True.
That’s why an empty list is always False while a list with at least one element is True.
Suppose that you have a function that returns a list or None. The result list can have zero or more elements:
def get_list():
# ...Code language: Python (python)To display the elements of the list, you may come up with the following code:
my_list = get_list()
if my_list is not None and len(my_list) > 0:
for element in my_list:
print(element)
else:
print('List is None or empty')Code language: Python (python)The condition in the if clause makes sure that my_list is not None or empty.
However, this condition is unnecessary because you can shorten it like this. The code works the same:
my_list = get_list()
if my_list:
for element in my_list:
print(element)
else:
print('List is None or empty')Code language: Python (python)In this case, if the my_list is None or empty, then Python evaluates it to False.
Finally, if a class that doesn’t have both __bool__() and __len__() methods, the instances of that class always evaluate to True.
The following flowchart illustrates how the bool() works:
Summary #
- Python uses the
boolclass to represent boolean values:TrueandFalse. TrueandFalseare instances of theboolclass. In fact, they’re singleton objects of theboolclass.- Every object has a boolean value, which can be
TrueorFalse. Thebool(object)returns the Boolean value of theobj. - Under the hood the
bool()returns a Boolean value by calling the__bool__()or__len__()method of the object. If both methods don’t exist, the bool() returnsTrue.