Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create a slider using the Tkinter Scale widget.
Introduction to Tkinter slider widget #
A slider allows you to enter a value by moving an indicator. A slider can be vertical or horizontal:
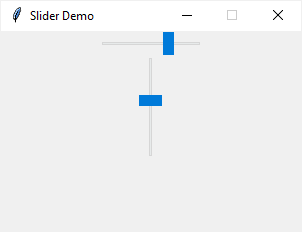
To create a slider, you’ll use the ttk.Scale() constructor as follows:
ttk.Scale(container,from_,to)Code language: Python (python)In this syntax, the container specifies the parent component of the slider.
The from_ and to options specify the minimum and maximum values of the slider. Since from is a keyword in Python, Tkinter uses from_ instead.
By default, a slider is horizontal. To specify how the slider is arranged, you use the orient option which can be horizontal or vertical. For example:
slider = ttk.Scale(
root,
from_=0,
to=100,
orient='vertical', # horizontal
)Code language: Python (python)Getting current value #
To get the current value of the slider, you can assign a DoubleVar to the variable of the slider like this:
current_value = tk.DoubleVar()
slider = ttk.Scale(
root,
from_=0,
to=100,
orient='horizontal',
variable=current_value
)Code language: Python (python)Another way to get the current value of slider is to call the get() method of the slider object:
slider.get()Code language: Python (python)Executing a callback #
To run a function whenever the value of the slider changes, you can assign it to the command option as follows:
def slider_changed(event):
print(slider.get())
slider = ttk.Scale(
root,
from_=0,
to=100,
orient='horizontal',
variable=current_value
command=slider_changed
)
Code language: Python (python)Notice that calling a function when the value of the slider changes can cause performance problems.
Disabling the slider #
To disable the slider, you set its state to 'disabled'. To re-enable it, you set its state to 'normal'.
slider['state'] = 'disabled'
slider['state'] = 'normal'Code language: Python (python)By default, the slider’s state is 'normal'.
Tkinter slider example #
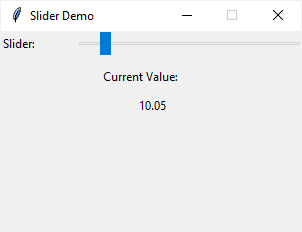
The following program illustrates how to use a Tkinter slider widget. The label will update the current value of the slider when you change the slider’s value.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# root window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('300x200')
root.resizable(False, False)
root.title('Slider Demo')
root.columnconfigure(0, weight=1)
root.columnconfigure(1, weight=3)
# slider current value
current_value = tk.DoubleVar()
def get_current_value():
return '{: .2f}'.format(current_value.get())
def slider_changed(event):
value_label.configure(text=get_current_value())
# label for the slider
slider_label = ttk.Label(
root,
text='Slider:'
)
slider_label.grid(
column=0,
row=0,
sticky='w'
)
# slider
slider = ttk.Scale(
root,
from_=0,
to=100,
orient='horizontal', # vertical
command=slider_changed,
variable=current_value
)
slider.grid(
column=1,
row=0,
sticky='we'
)
# current value label
current_value_label = ttk.Label(
root,
text='Current Value:'
)
current_value_label.grid(
row=1,
columnspan=2,
sticky='n',
ipadx=10,
ipady=10
)
# value label
value_label = ttk.Label(
root,
text=get_current_value()
)
value_label.grid(
row=2,
columnspan=2,
sticky='n'
)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
Summary #
- Use the
ttk.Scale()to create a slider widget. - Use the
scale.get()or thevariableoption to get the current value of the slider. - Use the
commandoption to assign a function that will execute when the slider’s value changes.